Effect of chirality on cellular uptake, imaging and photodynamic therapy of photosensitizers derived from chlorophyll-a
- PMID: 25936263
- PMCID: PMC4461543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.04.006
Effect of chirality on cellular uptake, imaging and photodynamic therapy of photosensitizers derived from chlorophyll-a
Abstract
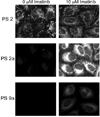
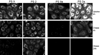
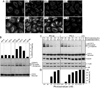
We have previously shown that the (124)I-analog of methyl 3-(1'-m-iodobenzyloxy) ethyl-3-devinyl-pyropheophorbide-a derived as racemic mixture from chlorophyll-a can be used for PET (positron emission tomography)-imaging in animal tumor models. On the other hand, as a non-radioactive analog, it showed excellent fluorescence and photodynamic therapy (PDT) efficacy. Thus, a single agent in a mixture of radioactive ((124)I-) and non-radioactive ((127)I) material can be used for both dual-imaging and PDT of cancer. Before advancing to Phase I human clinical trials, we evaluated the activity of the individual isomers as well as the impact of a chiral center at position-3(1) in directing in vitro/in vivo cellular uptake, intracellular localization, epithelial tumor cell-specific retention, fluorescence/PET imaging, and photosensitizing ability. The results indicate that both isomers (racemates), either as methyl ester or carboxylic acid, were equally effective. However, the methyl ester analogs, due to subcellular deposition into vesicular structures, were preferentially retained. All derivatives containing carboxylic acid at the position-17(2) were noted to be substrate for the ABCG2 (a member of the ATP binding cassette transporters) protein explaining their low retention in lung tumor cells expressing this transporter. The compounds in which the chirality at position-3 has been substituted by a non-chiral functionality showed reduced cellular uptake, retention and lower PDT efficacy in mice bearing murine Colon26 tumors.
Keywords: Cell-specificity; Chlorophyll-a; Imaging; Photodynamic therapy; Photosensitizer.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
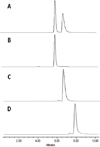
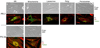
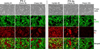

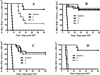
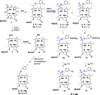
 ) and 128J/cm2, 14 mW/cm2, (
) and 128J/cm2, 14 mW/cm2, ( )]. (B): PS 2 and the corresponding R- and S- isomers 3, 4; (C): isomers 5 and 6 and, (D): PS 2 and PS. 9 (achiral at position-3). All animals in B to D were treated with 665 nm light (128J/cm2, 14 mW/cm2), Tumor growth was monitored daily for 60 days.
)]. (B): PS 2 and the corresponding R- and S- isomers 3, 4; (C): isomers 5 and 6 and, (D): PS 2 and PS. 9 (achiral at position-3). All animals in B to D were treated with 665 nm light (128J/cm2, 14 mW/cm2), Tumor growth was monitored daily for 60 days.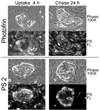
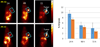
References
-
- Aboul-Enein H, Wainer IW. In: The impact of stereochemistry on drug development and use, vol. 142 in Chemical Analysis. A series of Monographs on Analytical Chemistry and its applications. Winefordner JD, editor. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1987.
-
- William IW, editor. Drug Stereochemistry: Analytical Methods and Pharmacology. 2nd ed. New Work: Marcel Dekker; 1993. and references therein.
-
- Wilson K, Walker J, editors. Chirality and its importance in drug development. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1991;19:444–475. - PubMed
-
- Rettie AE, Korzekwa KR, Kunze KL, Lawrence RF, Eddy AC, Aoyama T, Gelboin HV, Gonzalez FJ, Trager WF. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1992;5:54. - PubMed
-
- Knoche B, Blaschke G. Chirality. 1994;6:221.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

