Prediction of respiratory disease and diarrhea in veal calves based on immunoglobulin levels and the serostatus for respiratory pathogens measured at arrival
- PMID: 25937168
- PMCID: PMC7114331
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2015.04.009
Prediction of respiratory disease and diarrhea in veal calves based on immunoglobulin levels and the serostatus for respiratory pathogens measured at arrival
Abstract
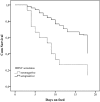
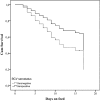
Failure of passive transfer is a common problem in calves destined for veal production. At present it is unknown whether the risk for respiratory disease (BRD) or neonatal calf diarrhea (NCD) in the veal herd is associated with total immunoglobulin (Ig) and/or on the serostatus for respiratory pathogens measured at arrival. Therefore, the first objective of this prospective longitudinal cohort study was to determine associations between serum protein fractions as determined by routine electrophoresis (total protein, albumin, alpha-1 and -2 globulins, beta-globulins and Ig's) at arrival and BRD and NCD in the first 3 weeks of the production cycle. The second objective was to determine whether the serostatus (seropositive/seronegative) of seven respiratory pathogens (bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV), parainfluenzavirus-3, bovine coronavirus (BCV), bovine herpesvirus-1, bovine viral diarrhea virus, Mannheimia haemolytica and Mycoplasma bovis) of these arrival serum samples could be associated with the risk of having BRD. The third objective was to determine which of the electrophoresis proteins and respiratory serostatuses were associated with average daily gain (ADG) in the study period. The study population consisted of 150 rosé veal calves housed in a single air-space. The study period ended at day 18 post arrival, when BRD incidence was judged to be too high to further postpone a group treatment. A Cox regression model was used to determine the effect of the studied protein fractions and antibodies on the time to BRD and NCD occurrence. The effect of the studied predictors on ADG was determined by linear regression. Calves with Ig levels under 7.5g/L had an increased BRD hazard (hazard ratio (HR)=1.9 (95% confidence interval (CI)=1.2-3.0)). NCD was only positively associated with the alpha-2 globulin concentration. Calves with a negative serostatus for BCV (HR=1.7 (95% CI=1.0-2.8)) or BRSV (HR=2.0 (95% CI=1.0-3.9)) had an increased BRD hazard. Average daily gain (ADG) was 0.242kg/day (SD=0.142) and was not related to the occurrence of BRD or NCD. Calves with Ig's below 7.5g/L and with increased levels of alpha-2 globulins showed a decrease in ADG. This study showed the importance of providing sufficient colostrum to veal calves and the potential benefit of the presence of BCV and BRSV antibodies at arrival to reduce the BRD hazard in the first 3 weeks.
Keywords: Average daily gain; Bovine respiratory disease; Failure of passive transfer; Immunoglobulin; Neonatal diarrhea; Veal calves.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Barnes D.M., Song Z., Klasing K.C., Bottje W. Protein metabolism during an acute phase response in chickens. Amino Acids. 2002;22:15–26. - PubMed
-
- BCFI . 2013. Commented Drug Repertorium for Veterinary Use. Ed.: Belgian Center for Pharmacotherapeutic Information, P. Gustin, Ghent, Belgium. www.bcfi-vet.be (accessed 03.06.14)
-
- Berge A.C., Lindeque P., Moore D.A., Sischo W.M. A clinical trail evaluating prophylactic and therapeutic antibiotic use on health and performance of preweaned calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2005;88:2166–2177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

