An integrated metabonomic and proteomic study on Kidney-Yin Deficiency Syndrome patients with diabetes mellitus in China
- PMID: 25937635
- PMCID: PMC4594178
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2014.169
An integrated metabonomic and proteomic study on Kidney-Yin Deficiency Syndrome patients with diabetes mellitus in China
Abstract
Aim: To investigate specific changes in metabolites and proteins of Kidney-Yin Deficiency Syndrome (KYDS) patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) in China.
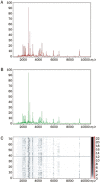
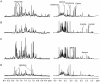
Methods: KYDS (n=29) and non-KYDS (n=23) patients with DM were recruited for this study. The KYDS was diagnosed by two senior TCM clinicians separately. The metabonomic and proteomic profiles of the patients were assessed using a metabonomic strategy based on NMR with multivariate analysis and a proteomic strategy based on MALDI-TOF-MS, respectively.
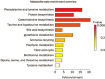
Results: Eighteen upregulated peptides and thirty downregulated peptides were observed in the plasma of the KYDS patients. Comparing the proteomic profiles of the KYDS and non-KYDS groups, however, no significantly differentially expressed peptides were found. At the same time, major metabolic alterations were found to distinguish the two groups, including eight significantly changed metabolites (creatinine, citrate, TMAO, phenylalanine, tyrosine, alanine, glycine and taurine). The levels of creatinine, citrate, TMAO, phenylalanine and tyrosine were decreased, whereas the levels of alanine, glycine and taurine were increased in the KYDS patients. These biochemical changes were found to be associated with alterations in amino acid metabolism, energy metabolism and gut microflora.
Conclusion: The identification of distinct expression profiles of metabolites and signaling pathways in KYDS patients with DM suggests that there are indeed molecular signatures underlying the principles of 'Syndrome Differentiation' in traditional Chinese medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated Systems Pharmacology, Urinary Metabonomics, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis to Uncover Targets and Metabolic Pathways of the You-Gui Pill in Treating Kidney-Yang Deficiency Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 26;20(15):3655. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153655. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31357410 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiling reveals therapeutic biomarkers of processed Aconitum carmichaeli Debx in treating hydrocortisone induced kidney-yang deficiency syndrome rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 28;152(3):585-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.011. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24556226
-
Screening and identification of potential biomarkers and establishment of the diagnostic serum proteomic model for the Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndromes of tuberculosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1322-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.07.025. Epub 2014 Jul 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25072359
-
Advances in Research on Diabetes by Human Nutriomics.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 29;20(21):5375. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215375. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31671732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic and metabolomic profiles in atherothrombotic vascular disease.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2010 May;12(3):202-8. doi: 10.1007/s11883-010-0102-y. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2010. PMID: 20425260 Review.
Cited by
-
Mass spectrometry-based metabolomic as a powerful tool to unravel the component and mechanism in TCM.Chin Med. 2025 May 12;20(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01112-2. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40355943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fangjiomics: revealing adaptive omics pharmacological mechanisms of the myriad combination therapies to achieve personalized medicine.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Jun;36(6):651-3. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.33. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 26036241 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of Zuo-Gui Yin Decoction Effects on Six CYP450 Enzymes in Rats Using a Cocktail Method by UPLC-MS/MS.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Aug 26;2022:4293062. doi: 10.1155/2022/4293062. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36060135 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct common signatures of gut microbiota associated with damp-heat syndrome in patients with different chronic liver diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1027628. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1027628. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36467028 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine attenuates arsenic-induced pyroptosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting the autophagic-inflammasomal pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 20;9(10):946. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1004-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30237538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1Ma T, Tan CG, Zhang H, Wang MQ, Ding WJ, Li S. Bridging the gap between traditional Chinese medicine and systems biology: the connection of Cold Syndrome and NEI network. Mol Biosystems 2010; 6: 613–9. - PubMed
-
- 5Nicholson JK, Connelly J, Lindon JC, Holmes E. Metabonomics: a platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002; 1: 153–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

