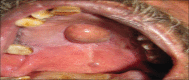
Osteolipoma of the palate - An unusual presentation
- PMID: 25937752
- PMCID: PMC4405983
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-5950.154856
Osteolipoma of the palate - An unusual presentation
Figures
References
-
- Piattelli A, Fioroni M, Iezzi G, Rubini C. Osteolipoma of the tongue. Oral Oncol. 2001;37:468–70. - PubMed
-
- Fregnani ER, Pires FR, Falzoni R, Lopes MA, Vargas PA. Lipomas of the oral cavity: Clinical findings, histological classification and proliferative activity of 46 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;32:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Furlong MA, Fanburg-Smith JC, Childers EL. Lipoma of the oral and maxillofacial region: Site and subclassification of 125 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;98:441–50. - PubMed
-
- Adebiyi KE, Ugboko VI, Maaji SM, Ndubuizu G. Osteolipoma of the palate: Report of a case and review of the literature. Niger J Clin Pract. 2011;14:242–4. - PubMed
-
- de Castro Al, de Castro EV, Felipini RC, Riberio AC, Soubhia AM. Osteolipoma of the buccal mucosa. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010;15:e347–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources