Therapeutic effects of topical netrin-4 in a corneal acute inflammatory model
- PMID: 25938032
- PMCID: PMC4413598
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.02.03
Therapeutic effects of topical netrin-4 in a corneal acute inflammatory model
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of netrin-4 on the early acute phase of inflammation in the alkali-burned eye.
Methods: Eye drops containing netrin-4 or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) were administered to a alkali-burn-induced corneal acute inflammatory model four times daily. The clinical evaluations, including fluorescein staining and inflammatory index, were performed on day 1, 4 and 7 using slit lamp microscopy. Global specimens were collected on day 7 and processed for immunofluorescent staining. The levels of inflammatory mediators in the corneas were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
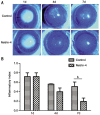
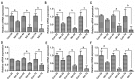
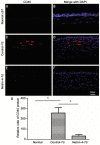
Results: Exogenous netrin-4 administered on rat ocular surfaces showed more improvements in decreasing fluorescein staining on day 4 and 7, and resolved alkali burn-induced corneal inflammation index on day 7 (P<0.01). The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 (MIP-1) in corneas were decreased in netrin-4-treated groups (P<0.05). In addition, netrin-4 significantly reduced the expression of leukocyte common antigen 45 (CD45) in the alkali-burn cornea (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Topical netrin-4 accelerated wound healing and reduced the inflammation on alkali-burn rat model, suggesting a potential as an anti-inflammatory agent in the clinical to treat the acute inflammation.
Keywords: alkali burn; cornea; inflammation; netrin-4.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Netrin-1 simultaneously suppresses corneal inflammation and neovascularization.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Mar 9;53(3):1285-95. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8722. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22323486
-
The role of pirfenidone in alkali burn rat cornea.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Nov;64:78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.08.032. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30153530
-
Thymosin beta 4 promotes corneal wound healing and decreases inflammation in vivo following alkali injury.Exp Eye Res. 2002 Feb;74(2):293-9. doi: 10.1006/exer.2001.1125. Exp Eye Res. 2002. PMID: 11950239
-
Efficacy of the nucleotide-binding oligomerzation domain 1 inhibitor Nodinhibit-1 on corneal alkali burns in rats.Int J Ophthalmol. 2015 Oct 18;8(5):860-5. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.05.02. eCollection 2015. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26558192 Free PMC article.
-
Aloe Vera Gel-derived Eye Drops for Alkaline Corneal Injury in a Rabbit Model.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020 Feb 2;15(1):7-15. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v15i1.5932. eCollection 2020 Jan-Mar. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020. PMID: 32095203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lack of netrin-4 alters vascular remodeling in the retina.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019 Oct;257(10):2179-2184. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04447-3. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31451908
-
Netrin-1 promotes epithelium repair in corneal injury.Int J Ophthalmol. 2020 Feb 18;13(2):206-212. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2020.02.02. eCollection 2020. Int J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32090028 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Role of Netrin-4 in Diabetic Retinopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 25;22(9):4481. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094481. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33923095 Free PMC article.
-
Structural decoding of netrin-4 reveals a regulatory function towards mature basement membranes.Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 30;7:13515. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13515. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27901020 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression and molecular analysis of recombinant Netrin-A protein of Lucilia sericata Meigen (Diptera: Calliphoridae) larvae.SAGE Open Med. 2024 Jan 29;12:20503121231223607. doi: 10.1177/20503121231223607. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med. 2024. PMID: 38292417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saika S, Miyamoto T, Yamanaka O, Kato T, Ohnishi Y, Flanders KC, Ikeda K, Nakajima Y, Kao WW, Sato M, Muragaki Y, Ooshima A. Therapeutic effect of topical administration of SN50, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB, in treatment of corneal alkali burns in mice. Am J Pathol. 2005;166(5):1393–1403. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Matsuda H, Wang L, Watanabe T, Kimura MT, Igarashi J, Wang X, Sakimoto T, Fukuda N, Sawa M, Nagase H. Pretranscriptional regulation of Tgf-beta1 by PI polyamide prevents scarring and accelerates wound healing of the cornea after exposure to alkali. Mol Ther. 2010;18(3):519–527. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Serafini T, Kennedy TE, Galko MJ, Mirzayan C, Jessell TM, Tessier-Lavigne M. The netrins define a family of axon outgrowth-promoting proteins homologous to C. elegans UNC-6. Cell. 1994;78(3):409–424. - PubMed
-
- Cirulli V, Yebra M. Netrins: beyond the brain. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(4):296–306. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
