False Discovery Rates in PET and CT Studies with Texture Features: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 25938522
- PMCID: PMC4418696
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124165
False Discovery Rates in PET and CT Studies with Texture Features: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Purpose: A number of recent publications have proposed that a family of image-derived indices, called texture features, can predict clinical outcome in patients with cancer. However, the investigation of multiple indices on a single data set can lead to significant inflation of type-I errors. We report a systematic review of the type-I error inflation in such studies and review the evidence regarding associations between patient outcome and texture features derived from positron emission tomography (PET) or computed tomography (CT) images.
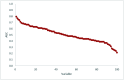
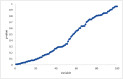
Methods: For study identification PubMed and Scopus were searched (1/2000-9/2013) using combinations of the keywords texture, prognostic, predictive and cancer. Studies were divided into three categories according to the sources of the type-I error inflation and the use or not of an independent validation dataset. For each study, the true type-I error probability and the adjusted level of significance were estimated using the optimum cut-off approach correction, and the Benjamini-Hochberg method. To demonstrate explicitly the variable selection bias in these studies, we re-analyzed data from one of the published studies, but using 100 random variables substituted for the original image-derived indices. The significance of the random variables as potential predictors of outcome was examined using the analysis methods used in the identified studies.
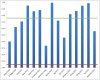
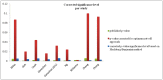
Results: Fifteen studies were identified. After applying appropriate statistical corrections, an average type-I error probability of 76% (range: 34-99%) was estimated with the majority of published results not reaching statistical significance. Only 3/15 studies used a validation dataset. For the 100 random variables examined, 10% proved to be significant predictors of survival when subjected to ROC and multiple hypothesis testing analysis.
Conclusions: We found insufficient evidence to support a relationship between PET or CT texture features and patient survival. Further fit for purpose validation of these image-derived biomarkers should be supported by appropriate biological and statistical evidence before their association with patient outcome is investigated in prospective studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein IH (1973) Textural Features for Image Classification. Systems, Man and Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions on SMC-3: 610–621.
-
- Amadasun M, King R (1989) Textural features corresponding to textural properties. Systems, Man and Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions on 19: 1264–1274.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

