Aβ(1-42) fibril structure illuminates self-recognition and replication of amyloid in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 25938662
- PMCID: PMC4476499
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2991
Aβ(1-42) fibril structure illuminates self-recognition and replication of amyloid in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
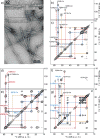
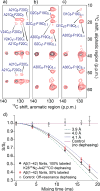
Increasing evidence has suggested that formation and propagation of misfolded aggregates of 42-residue human amyloid β (Aβ(1-42)), rather than of the more abundant Aβ(1-40), provokes the Alzheimer's disease cascade. However, structural details of misfolded Aβ(1-42) have remained elusive. Here we present the atomic model of an Aβ(1-42) amyloid fibril, from solid-state NMR (ssNMR) data. It displays triple parallel-β-sheet segments that differ from reported structures of Aβ(1-40) fibrils. Remarkably, Aβ(1-40) is incompatible with the triple-β-motif, because seeding with Aβ(1-42) fibrils does not promote conversion of monomeric Aβ(1-40) into fibrils via cross-replication. ssNMR experiments suggest that C-terminal Ala42, absent in Aβ(1-40), forms a salt bridge with Lys28 to create a self-recognition molecular switch that excludes Aβ(1-40). The results provide insight into the Aβ(1-42)-selective self-replicating amyloid-propagation machinery in early-stage Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

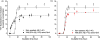
References
-
- Dobson CM. Protein folding and misfolding. Nature. 2003;426:884–890. - PubMed
-
- Petkova AT, et al. Self-propagating, molecular-level polymorphism in Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid fibrils. Science. 2005;307:262–265. - PubMed
Online Method References
-
- Chimon S, Ishii Y. Capturing intermediate structures of Alzheimer’s b-amyloid, Ab(1–40), by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:13472–13473. - PubMed
-
- Delaglio F, et al. Nmrpipe – a Multidimensional Spectral Processing System Based on Unix Pipes. J Biomol NMR. 1995;6:277–293. - PubMed
-
- Gullion T, Baker DB, Conradi MS. New, Compensated Carr-Purcell Sequences. J Magn Reson. 1990;89:479–484.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

