C-Peptide-based assessment of insulin secretion in the Zucker Fatty rat: a modelistic study
- PMID: 25938808
- PMCID: PMC4418729
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125252
C-Peptide-based assessment of insulin secretion in the Zucker Fatty rat: a modelistic study
Abstract
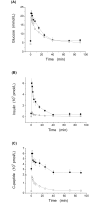
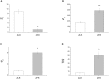
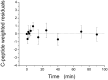
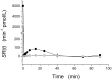
A C-peptide-based assessment of β-cell function was performed here in the Zucker fatty rat, a suitable animal model of human metabolic syndrome. To this aim, a 90-min intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT) was performed in seven Zucker fatty rats (ZFR), 7-to-9 week-old, and seven age-matched Zucker lean rats (ZLR). The minimal model of C-peptide (CPMM), originally introduced for humans, was adapted to Zucker rats and then applied to interpret IVGTT data. For a comprehensive evaluation of glucose tolerance in ZFR, CPMM was applied in combination with the minimal model of glucose kinetics (GKMM). Our results showed that the present CPMM-based interpretation of data is able to: 1) provide a suitable fit of C-Peptide data; 2) achieve a satisfactory estimation of parameters of interest 3) quantify both insulin secretion by estimating the time course of pre-hepatic secretion rate, SR(t), and total insulin secretion, TIS, and pancreatic sensitivity by means of three specific indexes of β-cell responsiveness to glucose stimulus (first-phase, Ф(1), second-phase, Ф(2), and steady-state, Ф(ss), never assessed in Zucker rats before; 4) detect the significant enhancement of insulin secretion in the ZFR, in face of a severe insulin-resistant state, previously observed only using a purely experimental approach. Thus, the methodology presented here represents a reliable tool to assess β-cell function in the Zucker rat, and opens new possibilities for the quantification of further processes involved in glucose homeostasis such as the hepatic insulin degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bray GA (1977) The Zucker-fatty rat: a review. Fed Proc 36:148–153. - PubMed
-
- Kurtz TW, Morris RC, Pershadsingh HA (1989) The Zucker fatty rat as a genetic model of obesity and hypertension. Hypertension 13: 896–901. - PubMed
-
- She P, Olson KC, Kadota Y, Inukai A, Shimomura Y, Hoppel CL, et al. (2013) Leucine and protein metabolism in obese Zucker rats. PLOS One 8(3): e59443 doi: 10.1371/ journal.pone.0059443 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siwy J, Zoja C, Klein J, Benigni A, Mullen W, Mayer B, et al. (2012) Evaluation of the Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rat as a model for human disease based on urinary peptidomic profiles. PLOS One 7(12): e51334 doi: 10.1371/ journal.pone.0051334 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burattini L, Burattini R, Cogo CE, Faelli E, Ruggeri P (2006) Power spectrum analysis of heart-rate variability in the young Zucker rat. Computers in Cardiology 33,4511794: 85–88.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

