The Yin and Yang of R-loop biology
- PMID: 25938907
- PMCID: PMC4522345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.04.008
The Yin and Yang of R-loop biology
Abstract
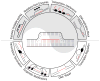
RNA performs diverse functions in cells, directing translation, modulating transcription and catalyzing enzymatic reactions. Remarkably RNA can also anneal to its genomic template co- or post-transcriptionally to generate an RNA-DNA hybrid and a displaced single-stranded DNA. These unusual nucleic acid structures are called R-loops. Studies in the last decades concentrated on the detrimental effects of R-loop formation, particularly on genome stability. In fact, R-loops are thought to play a role in several human diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative syndromes. But recent data has revealed that R-loops can also have a positive impact on cell processes, like regulating gene expression, chromosome structure and DNA repair. Here we summarize our current understanding of the formation and dissolution of R-loops, and discuss their negative and positive impact on genome structure and function.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
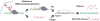
Similar articles
-
Detection and Characterization of R Loop Structures.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1543:231-242. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6716-2_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28349431
-
The dark side of RNA:DNA hybrids.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020 Apr-Jun;784:108300. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2020.108300. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32430097 Review.
-
R-Loop Physiology and Pathology: A Brief Review.DNA Cell Biol. 2020 Nov;39(11):1914-1925. doi: 10.1089/dna.2020.5906. Epub 2020 Oct 14. DNA Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33052725
-
R-Loops as Cellular Regulators and Genomic Threats.Mol Cell. 2019 Feb 7;73(3):398-411. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.024. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30735654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
R loops: new modulators of genome dynamics and function.Nat Rev Genet. 2015 Oct;16(10):583-97. doi: 10.1038/nrg3961. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Nat Rev Genet. 2015. PMID: 26370899 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA damage, inflammation and aging: Insights from mice.Front Aging. 2022 Sep 7;3:973781. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.973781. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 36160606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative, Convenient, and Efficient Genome-Wide R-Loop Profiling by ssDRIP-Seq in Multiple Organisms.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2528:445-464. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2477-7_29. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35704209
-
Characterization of functional relationships of R-loops with gene transcription and epigenetic modifications in rice.Genome Res. 2019 Aug;29(8):1287-1297. doi: 10.1101/gr.246009.118. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 31262943 Free PMC article.
-
One, No One, and One Hundred Thousand: The Many Forms of Ribonucleotides in DNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 2;21(5):1706. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051706. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32131532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathways and Mechanisms that Prevent Genome Instability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2017 Jul;206(3):1187-1225. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.145805. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28684602 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguilera A, Garcia-Muse T. R loops: from transcription byproducts to threats to genome stability. Mol Cell. 2012;46:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Westover KD, Bushnell DA, Kornberg RD. Structural basis of transcription: nucleotide selection by rotation in the RNA polymerase II active center. Cell. 2004;119:481–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

