Plant Sterols, Stanols, and Sitosterolemia
- PMID: 25941971
- PMCID: PMC4514516
- DOI: 10.5740/jaoacint.SGEAjagbe
Plant Sterols, Stanols, and Sitosterolemia
Abstract
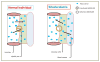
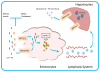
Phytosterolemia (sitosterolemia) is a rare autosomal recessive sterol storage disease caused by mutations in either of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding cassette transporter genes; (ABC) G5 or ABCG8, leading to impaired elimination of plant sterols and stanols, with their increased accumulation in the blood and tissues. Thus the disease is characterized by substantially elevated serum plant sterols and stanols, with moderate to high plasma cholesterol levels, and increased risk of premature atherosclerosis. Hematologic abnormalities including macrothrombocytopenia, stomatocytosis and hemolysis are frequently observed in sitosterolemia patients. Currently, ezetimibe, a sterol absorption inhibitor, is used as the routine treatment for sitosterolemia, with reported improvement in plant sterol levels and hemolytic parameters. This review summarizes the research related to the health impact of plant sterols and stanols on sitosterolemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific macrothrombocytopenia/hemolytic anemia associated with sitosterolemia.Am J Hematol. 2014 Mar;89(3):320-4. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23619. Am J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24166850
-
Two novel variants of the ABCG5 gene cause xanthelasmas and macrothrombocytopenia: a brief review of hematologic abnormalities of sitosterolemia.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Sep;15(9):1859-1866. doi: 10.1111/jth.13777. Epub 2017 Aug 5. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28696550 Review.
-
Platelet hyperreactivity explains the bleeding abnormality and macrothrombocytopenia in a murine model of sitosterolemia.Blood. 2013 Oct 10;122(15):2732-42. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-510461. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23926302 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic basis and hematologic manifestations of sitosterolemia in a group of Turkish patients.J Clin Lipidol. 2021 Sep-Oct;15(5):690-698. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 10. J Clin Lipidol. 2021. PMID: 34304999
-
[Sitosterolemia (phytosterolemia)].Internist (Berl). 2019 Aug;60(8):871-877. doi: 10.1007/s00108-019-0635-2. Internist (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31254003 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Chemical and Biochemical Features of Spinasterol and Schottenol.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1440:45-55. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-43883-7_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38036874
-
Progress and perspectives in plant sterol and plant stanol research.Nutr Rev. 2018 Oct 1;76(10):725-746. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy032. Nutr Rev. 2018. PMID: 30101294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical features and genetic analysis of childhood sitosterolemia: Two case reports and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(15):e15013. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015013. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30985648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oilseed crop sunflower (Helianthus annuus) as a source of food: Nutritional and health benefits.Food Sci Nutr. 2020 Jul 31;8(9):4666-4684. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1783. eCollection 2020 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32994929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uptake of Vitamins D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, and D7 Solubilized in Mixed Micelles by Human Intestinal Cells, Caco-2, an Enhancing Effect of Lysophosphatidylcholine on the Cellular Uptake, and Estimation of Vitamins D' Biological Activities.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 29;13(4):1126. doi: 10.3390/nu13041126. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33805560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel SB, Salen G, Hidaka H, Kwiterovich PO, Stalenhoef AF, Miettinen TA, Grundy SM, Lee MH, Rubenstein JS, Polymeropoulos MH, Brownstein MJ. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:1041–1044. http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI3963. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya AK, Connor WE. J Clin Invest. 1974;53:1033–1043. http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI107640. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shulman RS, Bhattacharyya AK, Connor WE, Fredrickson DS. New Engl J Med. 1976;294:482–483. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197602262940907. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berge KE, Tian H, Graf GA, Yu L, Grishin NV, Schultz J, Kwiterovich P, Shan B, Barnes R, Hobbs HH. Science. 2000;290:1771–1775. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5497.1771. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

