mTORC1 Regulates Flagellin-Induced Inflammatory Response in Macrophages
- PMID: 25942007
- PMCID: PMC4420466
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125910
mTORC1 Regulates Flagellin-Induced Inflammatory Response in Macrophages
Abstract
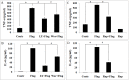
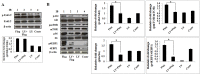
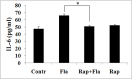
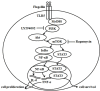
Bacterial flagellin triggers inflammatory responses. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) regulate the production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines that are induced by extrinsic antigens, but the function of mTORC1 in flagellin-induced inflammatory response is unknown. The purpose of this study was to examine the role and the mechanism of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in flagellin-induced cytokine expression in mouse macrophages. We observed that flagellin upregulated TNF-α time- and dose-dependently. Flagellin stimulated rapid (<15 min) PI3K/Akt/mTOR phosphorylation that was mediated by TLR5. Inhibition of PI3K with LY294002 and wortmannin, and of mTORC1 with rapamycin decreased flagellin-induced TNF-α and IL-6 expression and cell proliferation. The activation of NF-κB p65 and STAT3 was regulated by mTORC1 via degradation of IκBα and phosphorylation of STAT3 in response to flagellin, respectively. Thus, the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway regulates the innate immune response to bacterial flagellin. Rapamycin is potential therapy that can regulate host defense against pathogenic infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, et al. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature. 2001; 410: 1099–1103. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Hemmi H. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett. 2003; 85: 85–95. - PubMed
-
- Gewirtz AT, Navas TA, Lyons S, Godowski PJ, Madara JL. Cutting edge: bacterial flagellin activates basolaterally expressed TLR5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory gene expression. J Immunol. 2001; 167: 1882–1885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

