Prdx4 is a compartment-specific H2O2 sensor that regulates neurogenesis by controlling surface expression of GDE2
- PMID: 25943695
- PMCID: PMC4432624
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8006
Prdx4 is a compartment-specific H2O2 sensor that regulates neurogenesis by controlling surface expression of GDE2
Abstract
Neural progenitors and terminally differentiated neurons show distinct redox profiles, suggesting that coupled-redox cascades regulate the initiation and progression of neuronal differentiation. Discrete cellular compartments have different redox environments and how they contribute to differentiation is unclear. Here we show that Prdx4, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) enzyme that metabolizes H2O2, acts as a tunable regulator of neurogenesis via its compartmentalized thiol-oxidative function. Prdx4 ablation causes premature motor neuron differentiation and progenitor depletion, leading to imbalances in subtype-specific motor neurons. GDE2, a six-transmembrane protein that induces differentiation by downregulating Notch signalling through surface cleavage of GPI-anchored proteins, is targeted by Prdx4 oxidative activity. Prdx4 dimers generated by H2O2 metabolism oxidize two cysteine residues within the GDE2 enzymatic domain, which blocks GDE2 trafficking to the plasma membrane and prevents GDE2 neurogeneic function. Thus, Prdx4 oxidative activity acts as a sensor to directly couple neuronal differentiation with redox environments in the ER.
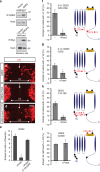
Figures






References
-
- Schafer F. Q. & Buettner G. R. Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 30, 1191–1212 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Putker M., Vos H. R. & Dansen T. B. Intermolecular disulfide-dependent redox signalling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 42, 971–978 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Holmström K. M. & Finkel T. Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 411–421 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

