Estrogen regulates luminal progenitor cell differentiation through H19 gene expression
- PMID: 25944846
- PMCID: PMC4498491
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-15-0105
Estrogen regulates luminal progenitor cell differentiation through H19 gene expression
Abstract
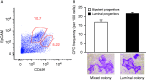
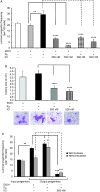
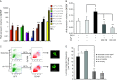
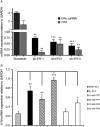
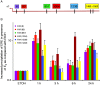
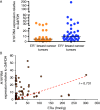
Although the role of estrogen signaling in breast cancer development has been extensively studied, the mechanisms that regulate the indispensable role of estrogen in normal mammary gland development have not been well studied. Because of the unavailability of culture system to maintain estrogen-receptor-positive (ERα(+)) cells in vitro, the molecular mechanisms that regulate estrogen/ERα signaling in the normal human breast are unknown. In the present study, we examined the effects of estrogen signaling on ERα(+) human luminal progenitors using a modified matrigel assay and found that estrogen signaling increased the expansion potential of these progenitors. Furthermore, we found that blocking ERα attenuated luminal progenitor expansion and decreased the luminal colony-forming potential of these progenitors. Additionally, blocking ERα decreased H19 expression in the luminal progenitors and led to the development of smaller luminal colonies. We further showed that knocking down the H19 gene in the luminal progenitors significantly decreased the colony-forming potential of the luminal progenitors, and this phenotype could not be rescued by the addition of estrogen. Lastly, we explored the clinical relevance of the estrogen-H19 signaling axis in breast tumors and found that ERα(+) tumors exhibited a higher expression of H19 as compared with ERα(-) tumors and that H19 expression showed a positive correlation with ERα expression in those tumors. Taken together, the present results indicate that the estrogen-ERα-H19 signaling axis plays a role in regulating the proliferation and differentiation potentials of the normal luminal progenitors and that this signaling network may also be important in the development of ER(+) breast cancer tumors.
Keywords: ER+ breast cancer cells; ERα; H19; luminal progenitors.
© 2015 The authors.
Figures
References
-
- Adriaenssens E, Dumont L, Lottin S, Bolle D, Lepretre A, Delobelle A, Bouali F, Dugimont T, Coll J, Curgy JJ. H19 overexpression in breast adenocarcinoma stromal cells is associated with tumor values and steroid receptor status but independent of p53 and Ki-67 expression. American Journal of Pathology. 1998;153:1597–1607. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65748-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adriaenssens E, Lottin S, Berteaux N, Hornez L, Fauquette W, Fafeur V, Peyrat JP, Le Bourhis X, Hondermarck H, Coll J, et al. Cross-talk between mesenchyme and epithelium increases H19 gene expression during scattering and morphogenesis of epithelial cells. Experimental Cell Research. 2002;275:215–229. doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5500. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

