FBXO32 Targets c-Myc for Proteasomal Degradation and Inhibits c-Myc Activity
- PMID: 25944903
- PMCID: PMC4481220
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.645978
FBXO32 Targets c-Myc for Proteasomal Degradation and Inhibits c-Myc Activity
Abstract
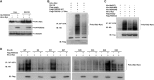
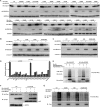
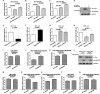
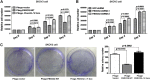
FBXO32 (MAFbx/Atrogin-1) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is markedly up-regulated in muscle atrophy. Although some data indicate that FBXO32 may play an important role in tumorigenesis, the molecular mechanism of FBXO32 in tumorigenesis has been poorly understood. Here, we present evidence that FBXO32 targets the oncogenic protein c-Myc for ubiquitination and degradation through the proteasome pathway. Phosphorylation of c-Myc at Thr-58 and Ser-62 is dispensable for FBXO32 to induce c-Myc degradation. Mutation of the lysine 326 in c-Myc reduces c-Myc ubiquitination and prevents the c-Myc degradation induced by FBXO32. Furthermore, overexpression of FBXO32 suppresses c-Myc activity and inhibits cell growth, but knockdown of FBXO32 enhances c-Myc activity and promotes cell growth. Finally, we show that FBXO32 is a direct downstream target of c-Myc, highlighting a negative feedback regulation loop between c-Myc and FBXO32. Thus, FBXO32 may function by targeting c-Myc. This work explains the function of FBXO32 and highlights its mechanisms in tumorigenesis.
Keywords: FBXO32; Myc (c-Myc); cell proliferation; muscle atrophy; oncogene; proteasomal degradation; ubiquitylation (ubiquitination).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Bodine S. C., Latres E., Baumhueter S., Lai V. K. M., Nunez L., Clarke B. A., Poueymirou W. T., Panaro F. J., Na E. Q., Dharmarajan K., Pan Z. Q., Valenzuela D. M., DeChiara T. M., Stitt T. N., Yancopoulos G. D., Glass D. J. (2001) Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294, 1704–1708 - PubMed
-
- Ponting C. P., Phillips C., Davies K. E., Blake D. J. (1997) PDZ domains: targeting signalling molecules to sub-membranous sites. Bioessays 19, 469–479 - PubMed
-
- Harrison S. C. (1996) Peptide-surface association: the case of PDZ and PTB domains. Cell 86, 341–343 - PubMed
-
- Julie L. C., Sabrina B. P., Marie-Pierre L., Leibovitch S. A. (2012) Identification of essential sequences for cellular localization in the muscle-specific ubiquitin E3 ligase MAFbx/Atrogin 1. FEBS Lett. 586, 362–367 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

