Chaperonin-containing t-complex protein-1 subunit β as a possible biomarker for the phase of glomerular hyperfiltration of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 25944975
- PMCID: PMC4402165
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/548101
Chaperonin-containing t-complex protein-1 subunit β as a possible biomarker for the phase of glomerular hyperfiltration of diabetic nephropathy
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Chaperonin-Containing t-Complex Protein-1 Subunit β as a Possible Biomarker for the Phase of Glomerular Hyperfiltration of Diabetic Nephropathy".Dis Markers. 2016;2016:8653290. doi: 10.1155/2016/8653290. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Dis Markers. 2016. PMID: 27069298 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
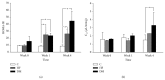
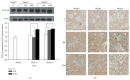
In cell model, we discovered the association between chaperonin-containing t-complex polypeptide 1 subunit β (TCP-1β) and early diabetic nephropathy (DN). In this study, we further explored the relationships between TCP-1β and type 2 diabetic mellitus (DM). To mimic the clinical hyperfiltration state, a type 2 DM mice model was established by feeding a high-fat diet in combination with treatment of streptozotocin and nicotinamide. Blood and urine were collected to determine creatinine clearance (C cr), and kidney tissues were harvested for evaluation of TCP-1β expression by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Meanwhile, clinical subjects of healthy controls and type 2 DM were recruited to strengthen the evidence with urine TCP-1β. Results showed that C cr and the expression of TCP-1β in kidney were significantly higher one week after hyperglycemia development, suggesting that the hyperfiltration state was successfully established in the mice model. TCP-1β was expressed predominantly on renal tubules. By using the estimated glomerular filtration rate to index progression in clinical investigation, urine TCP-1β level was associated with the hyperfiltration phase in type 2 DM patients. Conclusively, we confirmed that TCP-1β is a possible biomarker for early nephropathy of type 2 DM, but further mechanistic study to elucidate its cause and pathway is needed.
Figures

References
-
- Hwang J.-C., Chang L.-C., Lin Y.-F., Shui H.-A., Chen J.-S. Effects of fungal statins on high-glucose-induced mouse mesangial cell hypocontractility may involve filamentous actin, t-complex polypeptide 1 subunit beta, and glucose regulated protein 78. Translational Research. 2010;156(2):80–90. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2010.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

