Core-like groups result in invalidation of identifying super-spreader by k-shell decomposition
- PMID: 25946319
- PMCID: PMC5386204
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09602
Core-like groups result in invalidation of identifying super-spreader by k-shell decomposition
Abstract
Identifying the most influential spreaders is an important issue in understanding and controlling spreading processes on complex networks. Recent studies showed that nodes located in the core of a network as identified by the k-shell decomposition are the most influential spreaders. However, through a great deal of numerical simulations, we observe that not in all real networks do nodes in high shells are very influential: in some networks the core nodes are the most influential which we call true core, while in others nodes in high shells, even the innermost core, are not good spreaders which we call core-like group. By analyzing the k-core structure of the networks, we find that the true core of a network links diversely to the shells of the network, while the core-like group links very locally within the group. For nodes in the core-like group, the k-shell index cannot reflect their location importance in the network. We further introduce a measure based on the link diversity of shells to effectively distinguish the true core and core-like group, and identify core-like groups throughout the networks. Our findings help to better understand the structural features of real networks and influential nodes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
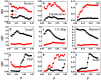
 (black squares), equal shell
(black squares), equal shell  (red circles) and upper shells
(red circles) and upper shells  (blue triangles) are represented. kS ranges from the smallest kS value to the largest kS value in the network.
(blue triangles) are represented. kS ranges from the smallest kS value to the largest kS value in the network.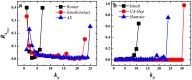
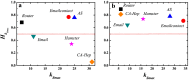
 is the largest kS value in the network.
is the largest kS value in the network.  is the link entropy of the innermost core.
is the link entropy of the innermost core.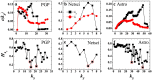
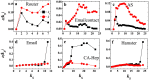
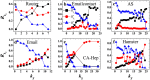
 is the link entropy of kS shell. Hollow red circles outline the shells which are densely connected core-like groups. These are 21-shell, 16-shell and 15-shell in PGP, 7-shell and 6-shell in Netsci and 48-shell and 30-shell in Astro. kS ranges from the smallest kS value to the largest kS value in the network.
is the link entropy of kS shell. Hollow red circles outline the shells which are densely connected core-like groups. These are 21-shell, 16-shell and 15-shell in PGP, 7-shell and 6-shell in Netsci and 48-shell and 30-shell in Astro. kS ranges from the smallest kS value to the largest kS value in the network.Similar articles
-
Improving the accuracy of the k-shell method by removing redundant links: From a perspective of spreading dynamics.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 17;5:13172. doi: 10.1038/srep13172. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26277903 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying a set of influential spreaders in complex networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 14;6:27823. doi: 10.1038/srep27823. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27296252 Free PMC article.
-
Locating influential nodes in complex networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 18;6:19307. doi: 10.1038/srep19307. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26776455 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying influential spreaders in complex networks by an improved gravity model.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 12;11(1):22194. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01218-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34772970 Free PMC article.
-
Super-spreaders: a historical review.Lancet Infect Dis. 2023 Oct;23(10):e409-e417. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00183-4. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37352877 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying and quantifying potential super-spreaders in social networks.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 15;9(1):14811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51153-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31616035 Free PMC article.
-
Super-Spreader Identification Using Meta-Centrality.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 23;6:38994. doi: 10.1038/srep38994. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 28008949 Free PMC article.
-
A model and simulation of the emotional contagion of netizens in the process of rumor refutation.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 2;9(1):14164. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50770-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31578405 Free PMC article.
-
Best influential spreaders identification using network global structural properties.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 26;11(1):2254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81614-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33500445 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the essential links in online commercial networks.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 29;6:34292. doi: 10.1038/srep34292. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27682464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kempe D., Kleinberg J. & Tordos . Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network. in Proc of the 9th ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. on knowledge discovery and data mining (ACM, Washington, DC, USA, 2003), KDD 03 137–146 (2003).
-
- Gallos L. K., Liljeros F., Argyrakis P., Bunde A. & Havlin S. Improving immunization strategies. Phys. Rev. E 75 045101(R) (2007). - PubMed
-
- Freeman L. C. Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Social Networks 1, 215–239 (1978).
-
- Freeman L. C. A set of measures of centrality based upon betweenness. Sociometry 40, 35–41 (1977).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

