Chemical Composition and Insecticidal Activity of Essential Oils from Zanthoxylum dissitum Leaves and Roots against Three Species of Storage Pests
- PMID: 25946557
- PMCID: PMC6272272
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20057990
Chemical Composition and Insecticidal Activity of Essential Oils from Zanthoxylum dissitum Leaves and Roots against Three Species of Storage Pests
Abstract
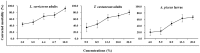
This work aimed to investigate chemical composition of essential oils obtained from Zanthoxylum dissitum leaves and roots and their insecticidal activities against several stored product pests, namely the cigarette beetle (Lasioderma serricorne), red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum) and black carpet beetle (Attagenus piceus). The analysis by GC-MS of the essential oils allowed the identification of 28 and 22 components, respectively. It was found that sesquiterpenoids comprised a fairly high portion of the two essential oils, with percentages of 74.0% and 80.9% in the leaves and roots, respectively. The main constituents identified in the essential oil of Z. dissitum leaves were δ-cadinol (12.8%), caryophyllene (12.7%), β-cubebene (7.9%), 4-terpineol (7.5%) and germacrene D-4-ol (5.7%), while humulene epoxide II (29.4%), caryophyllene oxide (24.0%), diepicedrene-1-oxide (10.7%) and Z,Z,Z-1,5,9,9-tetramethyl-1,4,7-cycloundecatriene (8.7%) were the major components in the essential oil of Z. dissitum roots. The insecticidal activity results indicated that the essential oil of Z. dissitum roots exhibited moderate contact toxicity against three species of storage pests, L. serricorne,T. castaneum and A. piceus, with LD50 values of 13.8, 43.7 and 96.8 µg/adult, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insecticidal and repellent efficacy against stored-product insects of oxygenated monoterpenes and 2-dodecanone of the essential oil from Zanthoxylum planispinum var. dintanensis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Aug;26(24):24988-24997. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05765-z. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31240663
-
Insecticidal Activities and Chemical Composition of the Essential Oils of Ajania nitida and Ajania nematoloba from China.J Oleo Sci. 2018 Dec 1;67(12):1571-1577. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess18102. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Oleo Sci. 2018. PMID: 30429442
-
Chemical constituents and insecticidal activities of the essential oil from Amomum tsaoko against two stored-product insects.J Oleo Sci. 2014;63(10):1019-26. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess14087. Epub 2014 Sep 10. J Oleo Sci. 2014. PMID: 25213443
-
From an Invasive Weed to an Insecticidal Agent: Exploring the Potential of Lantana camara in Insect Management Strategies-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 28;25(23):12788. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312788. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Oils Extracted from Different Species of the Lamiaceae Plant Family as Prospective Bioagents against Several Detrimental Pests.Molecules. 2020 Mar 28;25(7):1556. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071556. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32231104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
iORandLigandDB: A Website for Three-Dimensional Structure Prediction of Insect Odorant Receptors and Docking with Odorants.Insects. 2023 Jun 15;14(6):560. doi: 10.3390/insects14060560. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37367376 Free PMC article.
-
Repellent Activity of the Essential Oil from the Heartwood of Pilgerodendron uviferum (D. Don) Florin against Aegorhinus superciliosus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).Molecules. 2016 Apr 22;21(4):533. doi: 10.3390/molecules21040533. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27110756 Free PMC article.
-
Phytotoxic Potential of Zanthoxylum affine and Its Major Compound Linarin as a Possible Natural Herbicide.ACS Omega. 2018 Nov 30;3(11):14779-14787. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b02020. Epub 2018 Nov 2. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30555988 Free PMC article.
-
Brazilian essential oils as source for the discovery of new anti-COVID-19 drug: a review guided by in silico study.Phytochem Rev. 2021;20(5):1013-1032. doi: 10.1007/s11101-021-09754-4. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Phytochem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33867898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Constituents of Supercritical Extracts from Alpinia officinarum and the Feeding Deterrent Activity against Tribolium castaneum.Molecules. 2017 Apr 18;22(4):647. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040647. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28420198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo Z.N., Jia X.Q., Liu J.P., Liao J., Yang Y.F. Herbal medicines for advanced colorectal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012;5:CD004653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

