Adaptation, Commissioning, and Evaluation of a 3D Treatment Planning System for High-Resolution Small-Animal Irradiation
- PMID: 25948321
- PMCID: PMC4823181
- DOI: 10.1177/1533034615584522
Adaptation, Commissioning, and Evaluation of a 3D Treatment Planning System for High-Resolution Small-Animal Irradiation
Abstract
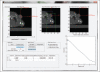
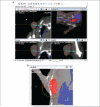
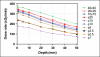
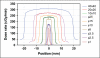
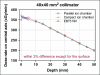
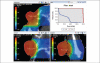
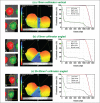
Although spatially precise systems are now available for small-animal irradiations, there are currently limited software tools available for treatment planning for such irradiations. We report on the adaptation, commissioning, and evaluation of a 3-dimensional treatment planning system for use with a small-animal irradiation system. The 225-kV X-ray beam of the X-RAD 225Cx microirradiator (Precision X-Ray) was commissioned using both ion-chamber and radiochromic film for 10 different collimators ranging in field size from 1 mm in diameter to 40 × 40 mm(2) A clinical 3-dimensional treatment planning system (Metropolis) developed at our institution was adapted to small-animal irradiation by making it compatible with the dimensions of mice and rats, modeling the microirradiator beam orientations and collimators, and incorporating the measured beam data for dose calculation. Dose calculations in Metropolis were verified by comparison with measurements in phantoms. Treatment plans for irradiation of a tumor-bearing mouse were generated with both the Metropolis and the vendor-supplied software. The calculated beam-on times and the plan evaluation tools were compared. The dose rate at the central axis ranges from 74 to 365 cGy/min depending on the collimator size. Doses calculated with Metropolis agreed with phantom measurements within 3% for all collimators. The beam-on times calculated by Metropolis and the vendor-supplied software agreed within 1% at the isocenter. The modified 3-dimensional treatment planning system provides better visualization of the relationship between the X-ray beams and the small-animal anatomy as well as more complete dosimetric information on target tissues and organs at risk. It thereby enhances the potential of image-guided microirradiator systems for evaluation of dose-response relationships and for preclinical experimentation generally.
Keywords: 3D dose distribution; commissioning; radiation therapy; small-animal irradiator; treatment planning system.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures
Similar articles
-
On the use of an analytic source model for dose calculations in precision image-guided small animal radiotherapy.Phys Med Biol. 2013 May 21;58(10):3377-95. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/58/10/3377. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Phys Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23615380
-
Dose painting by dynamic irradiation delivery on an image-guided small animal radiotherapy platform.Br J Radiol. 2019 Mar;92(1095):20180744. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180744. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30706718 Free PMC article.
-
Two-dimensional inverse planning and delivery with a preclinical image guided microirradiator.Med Phys. 2013 Oct;40(10):101709. doi: 10.1118/1.4819935. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 24089899
-
A review of treatment planning for precision image-guided photon beam pre-clinical animal radiation studies.Z Med Phys. 2014 Dec;24(4):323-34. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Z Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24629309 Review.
-
Small animal image-guided radiotherapy: status, considerations and potential for translational impact.Br J Radiol. 2015 Jan;88(1045):20140634. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140634. Br J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25387486 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the tumor registration error in biopsy procedures performed under real-time PET/CT guidance.Med Phys. 2017 Oct;44(10):5089-5095. doi: 10.1002/mp.12334. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28494089 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour and normal tissue radiobiology in mouse models: how close are mice to mini-humans?Br J Radiol. 2017 Jan;90(1069):20160441. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160441. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Br J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 27612010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Commissioning and performance characteristics of a pre-clinical image-guided radiotherapy system.Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2019 Jun;42(2):541-551. doi: 10.1007/s13246-019-00755-4. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2019. PMID: 30989595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin DS, Balis ME, Fisher B, et al. Role of murine tumor models in cancer treatment research. Cancer Res. 1986;46(4 pt 2):2189–2192. - PubMed
-
- Anisimov VN, Ukraintseva SV, Yashin AI. Cancer in rodents: does it tell us about cancer in humans? Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(10):807–819. - PubMed
-
- Kallman RF. Animal experiments in radiotherapy I—small animals. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1975;26(1):15–24. - PubMed
-
- Waterston RH, Lindblad-Toh K, Birney E, et al. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420(6915):520–562. - PubMed
-
- Yao R, Lecomte R, Crawford ES. Small-animal PET: what is it, and why do we need it? J Nucl Med Tech. 2012;40(3):157–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

