CDK-mediated RNF4 phosphorylation regulates homologous recombination in S-phase
- PMID: 25948581
- PMCID: PMC4477664
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv434
CDK-mediated RNF4 phosphorylation regulates homologous recombination in S-phase
Abstract
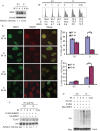
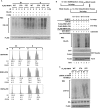
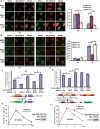
There are the two major pathways responsible for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs): non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR). NHEJ operates throughout the cell-cycle, while HR is primarily active in the S/G2 phases suggesting that there are cell cycle-specific mechanisms that regulate the balance between NHEJ and HR. Here we reported that CDK2 could phosphorylate RNF4 on T26 and T112 and enhance RNF4 E3 ligase activity, which is important for MDC1 degradation and proper HR repair during S phase. Mutation of the RNF4 phosphorylation sites results in MDC1 stabilization, which in turn compromised HR during S-phase. These results suggest that in addition to drive cell cycle progression, CDK also targets RNF4, which is involved in the regulatory network of DSBs repair.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA damage-induced sumoylation of Sp1 induces its interaction with RNF4 and degradation in S phase to remove 53BP1 from DSBs and permit HR.DNA Repair (Amst). 2022 Mar;111:103289. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2022.103289. Epub 2022 Feb 1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35124373
-
RNF4, a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin E3 ligase, promotes DNA double-strand break repair.Genes Dev. 2012 Jun 1;26(11):1179-95. doi: 10.1101/gad.188284.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22661229 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxin-3 consolidates the MDC1-dependent DNA double-strand break response by counteracting the SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase RNF4.EMBO J. 2017 Apr 13;36(8):1066-1083. doi: 10.15252/embj.201695151. Epub 2017 Mar 8. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28275011 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-dependent control of homologous recombination.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017 Aug 1;49(8):655-668. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmx055. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017. PMID: 28541389 Review.
-
Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice.Cell Res. 2008 Jan;18(1):134-47. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.111. Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18157161 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of trans-lesion synthesis (TLS) DNA polymerases in tumorigenesis and cancer therapy.NAR Cancer. 2023 Feb 6;5(1):zcad005. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcad005. eCollection 2023 Mar. NAR Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36755961 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-Targeted Ubiquitin Ligases and Their Functions in Maintaining Genome Stability.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 20;22(10):5391. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105391. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34065507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Ubiquitin, SUMO, and Poly(ADP-Ribose) in the Cellular Response to Genotoxic Stress.Front Genet. 2016 Apr 19;7:63. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00063. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27148359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A CK2-RNF4 interplay coordinates non-canonical SUMOylation and degradation of nuclear receptor FXR.J Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 1;9(3):195-208. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjx009. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28201649 Free PMC article.
-
In silico screening identifies a novel small molecule inhibitor that counteracts PARP inhibitor resistance in ovarian cancer.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 13;11(1):8042. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87325-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33850183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou B.B., Elledge S.J. The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 2000;408:433–439. - PubMed
-
- Lukas J., Lukas C., Bartek J. More than just a focus: The chromatin response to DNA damage and its role in genome integrity maintenance. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011;13:1161–1169. - PubMed
-
- Warmerdam D.O., Kanaar R. Dealing with DNA damage: relationships between checkpoint and repair pathways. Mutat. Res. 2010;704:2–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

