Synovial fluid hyaluronan mediates MSC attachment to cartilage, a potential novel mechanism contributing to cartilage repair in osteoarthritis using knee joint distraction
- PMID: 25948596
- PMCID: PMC4853581
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206847
Synovial fluid hyaluronan mediates MSC attachment to cartilage, a potential novel mechanism contributing to cartilage repair in osteoarthritis using knee joint distraction
Abstract
Objectives: Knee joint distraction (KJD) is a novel, but poorly understood, treatment for osteoarthritis (OA) associated with remarkable 'spontaneous' cartilage repair in which resident synovial fluid (SF) multipotential mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) may play a role. We hypothesised that SF hyaluronic acid (HA) inhibited the initial interaction between MSCs and cartilage, a key first step to integration, and postulate that KJD environment favoured MSC/cartilage interactions.
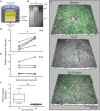
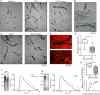
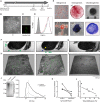
Methods: Attachment of dual-labelled SF-MSCs were assessed in a novel in vitro human cartilage model using OA and rheumatoid arthritic (RA) SF. SF was digested with hyaluronidase (hyase) and its effect on adhesion was observed using confocal microscopy. MRI and microscopy were used to image autologous dual-labelled MSCs in an in vivo canine model of KJD. SF-HA was investigated using gel electrophoresis and densitometry.
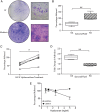
Results: Osteoarthritic-synovial fluid (OA-SF) and purified high molecular weight (MW) HA inhibited SF-MSC adhesion to plastic, while hyase treatment of OA-SF but not RA-SF significantly increased MSC adhesion to cartilage (3.7-fold, p<0.05) These differences were linked to the SF mediated HA-coat which was larger in OA-SF than in RA-SF. OA-SF contained >9 MDa HA and this correlated with increases in adhesion (r=0.880). In the canine KJD model, MSC adhesion to cartilage was evident and also dependent on HA MW.
Conclusions: These findings highlight an unappreciated role of SF-HA on MSC interactions and provide proof of concept that endogenous SF-MSCs are capable of adhering to cartilage in a favourable biochemical and biomechanical environment in OA distracted joints, offering novel one-stage strategies towards joint repair.
Keywords: Knee Osteoarthritis; Orthopedic Surgery; Osteoarthritis; Synovial fluid.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
References
-
- Saris DBF, Vanlauwe J, Victor J, et al. Treatment of symptomatic cartilage defects of the knee: characterized chondrocyte implantation results in better clinical outcome at 36 months in a randomized trial compared to microfracture. Am J Sports Med 2009;37(Suppl 1):10S–9S. 10.1177/0363546509350694 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

