Upregulation of UGT2B4 Expression by 3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-Phosphosulfate Synthase Knockdown: Implications for Coordinated Control of Bile Acid Conjugation
- PMID: 25948711
- PMCID: PMC4468435
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.114.061440
Upregulation of UGT2B4 Expression by 3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-Phosphosulfate Synthase Knockdown: Implications for Coordinated Control of Bile Acid Conjugation
Abstract
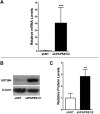
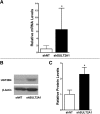
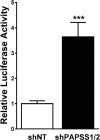
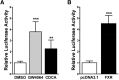
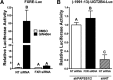
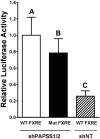
During cholestasis, the bile acid-conjugating enzymes, SULT2A1 and UGT2B4, work in concert to prevent the accumulation of toxic bile acids. To understand the impact of sulfotransferase deficiency on human hepatic gene expression, we knocked down 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate synthases (PAPSS) 1 and 2, which catalyze synthesis of the obligate sulfotransferase cofactor, in HepG2 cells. PAPSS knockdown caused no change in SULT2A1 expression; however, UGT2B4 expression increased markedly (∼41-fold increase in UGT2B4 mRNA content). Knockdown of SULT2A1 in HepG2 cells also increased UGT2B4 expression. To investigate the underlying mechanism, we transfected PAPSS-deficient HepG2 cells with a luciferase reporter plasmid containing ∼2 Kb of the UGT2B4 5'-flanking region, which included a response element for the bile acid-sensing nuclear receptor, farnesoid X receptor (FXR). FXR activation or overexpression increased UGT2B4 promoter activity; however, knocking down FXR or mutating or deleting the FXR response element did not significantly decrease UGT2B4 promoter activity. Further evaluation of the UGT2B4 5'-flanking region indicated the presence of distal regulatory elements between nucleotides -10090 and -10037 that negatively and positively regulated UGT2B4 transcription. Pulse-chase analysis showed that increased UGT2B4 expression in PAPSS-deficient cells was attributable to both increased mRNA synthesis and stability. Transfection analysis demonstrated that the UGT2B4 3'-untranslated region decreased luciferase reporter expression less in PAPSS-deficient cells than in control cells. These data indicate that knocking down PAPSS increases UGT2B4 transcription and mRNA stability as a compensatory response to the loss of SULT2A1 activity, presumably to maintain bile acid-conjugating activity.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Regulation of murine hepatic hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase expression in hyposulfatemic mice and in a cell model of 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate deficiency.Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 Aug;41(8):1505-13. doi: 10.1124/dmd.113.051912. Epub 2013 May 14. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23674610 Free PMC article.
-
FXR induces the UGT2B4 enzyme in hepatocytes: a potential mechanism of negative feedback control of FXR activity.Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1926-40. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)00388-3. Gastroenterology. 2003. PMID: 12806625
-
Suppression of DHEA sulfotransferase (Sult2A1) during the acute-phase response.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Oct;287(4):E731-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00130.2004. Epub 2004 Jun 15. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15198932
-
Bile salt excretory pump: biology and pathobiology.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006 Jul;43 Suppl 1:S10-6. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000226385.71859.5f. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16819395 Review.
-
Human 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) synthase: biochemistry, molecular biology and genetic deficiency.IUBMB Life. 2003 Jan;55(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/1521654031000072148. IUBMB Life. 2003. PMID: 12716056 Review.
Cited by
-
3,5-T2-an Endogenous Thyroid Hormone Metabolite as Promising Lead Substance in Anti-Steatotic Drug Development?Metabolites. 2022 Jun 23;12(7):582. doi: 10.3390/metabo12070582. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35888706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile acid indices as biomarkers for liver diseases I: Diagnostic markers.World J Hepatol. 2021 Apr 27;13(4):433-455. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i4.433. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33959226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araya Z, Wikvall K. (1999) 6α-hydroxylation of taurochenodeoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid by CYP3A4 in human liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1438:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Barbier O, Torra IP, Sirvent A, Claudel T, Blanquart C, Duran-Sandoval D, Kuipers F, Kosykh V, Fruchart JC, Staels B. (2003) FXR induces the UGT2B4 enzyme in hepatocytes: a potential mechanism of negative feedback control of FXR activity. Gastroenterology 124:1926–1940. - PubMed
-
- Barre L, Fournel-Gigleux S, Finel M, Netter P, Magdalou J, Ouzzine M. (2007) Substrate specificity of the human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT2B4 and UGT2B7. Identification of a critical aromatic amino acid residue at position 33. FEBS J 274:1256–1264. - PubMed
-
- Cartharius K, Frech K, Grote K, Klocke B, Haltmeier M, Klingenhoff A, Frisch M, Bayerlein M, Werner T. (2005) MatInspector and beyond: promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics 21:2933–2942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

