The dexmedetomidine "augmented" sedato analgesic cocktail: An effective approach for sedation in prolonged endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography
- PMID: 25948901
- PMCID: PMC4411834
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-9185.155149
The dexmedetomidine "augmented" sedato analgesic cocktail: An effective approach for sedation in prolonged endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography
Abstract
Background and aims: In absence of any published standard guideline for sedation or anesthesia practice for prolonged therapeutic "endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography (ERCP)", safe and cost-effective sedation protocol is the need of the hour. Our study aims to evaluate the efficacy of a dexmedetomidine as an add-on for prolonged deep sedation for ERCP and to compare three deep sedation regimens regarding safety and efficacy.
Material and methods: Forty-five consecutively enrolled patients planned for therapeutic ERCP and assumed to have prolonged procedural duration (>50 min) were divided into three groups in a randomized assessor blinded fashion. Group 1 received propofol and midazolam, Group 2 received the sedato-analgesic cocktail containing ketamine-propofol-midazolam-pentazocine, and the Group 3 received sedate-analgesic cocktail plus dexmedetomidine infusion under monitoring of vital parameters and according to the judgment of the concerned anesthesiologist. Total propofol requirement, episodes of gagging, oxygen desaturation, changes in mean blood pressure (MBP), recovery and satisfaction score of endoscopist, anesthetist and patient were noted and analyzed statistically using one way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction and Chi-square test.
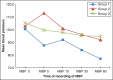
Results: Mean propofol requirement, incidences of gagging and oxygen desaturation was significantly less in Group 2 and 3 compared to Group 1. MBP was more stable and recovery was faster in Group 3. Anesthetist's satisfaction was more with Group 2 and even more with Group 3.
Conclusions: The sedato-analgesic cocktail was superior to the conventional propofol-midazolam regimen, dexmedetomidine as add-on increased the efficacy and safety of sedate-analgesic cocktail. It reduces propofol requirement, helps to maintain the patient in a safe and more stable level of sedation and increases satisfaction of the anesthetist.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography; ketamine; propofol; sedation; sedato-analgesic cocktail.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kapoor H. Anaesthesia for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55:918–26. - PubMed
-
- Orlewicz MS. Procedural Sedation. [Last accessed on 2013 Sep 15];2013 28:5. Available from: http://www.emedicine.medscape.com/article/109695-overview .
-
- Ong WC, Santosh D, Lakhtakia S, Reddy DN. A randomized controlled trial on use of propofol alone versus propofol with midazolam, ketamine, and pentazocine “sedato-analgesic cocktail” for sedation during ERCP. Endoscopy. 2007;39:807–12. - PubMed
-
- Muller S, Borowics SM, Fortis EA, Stefani LC, Soares G, Maguilnik I, et al. Clinical efficacy of dexmedetomidine alone is less than propofol for conscious sedation during ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:651–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous