Laser tattoo removal: a clinical update
- PMID: 25949017
- PMCID: PMC4411606
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2077.155066
Laser tattoo removal: a clinical update
Abstract
Techniques for tattoo removal have evolved significantly over the years. The commonly used Quality-switched (QS) ruby, alexandrite, and Nd:YAG lasers are the traditional workhorses for tattoo removal. Newer strategies using combination laser treatments, multi-pass treatments, and picosecond lasers offer promising results. The tattoo color and skin type of the patient are important considerations when choosing the appropriate laser. Standard protocols can be developed for the effective and safe treatment of tattoos.
Keywords: Picosecond lasers; Quality-switch lasers; Tattoo removal.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
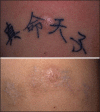
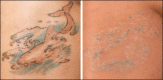



References
-
- Laumann AE, Derick AJ. Tattoos and body piercings in the United States: A national data set. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;55:413–21. - PubMed
-
- One in five US adults now has a tattoo. Harris Interactive Website. [Last accessed on 2014 Aug 15]. Available from: http://www.harrisinteractive.com/NewsRoom/HarrisPolls/tabid/447/ctl/Read... .
-
- Unwanted tattoos. ASDS website. [Last accessed on 2014 Aug 15]. Available from: https://www.asds.net/TattooRemovalInformation.aspx .
-
- Armstrong ML, Roberts AE, Koch JR, Saunders JC, Owen DC, Anderson RR. Motivation for contemporary tattoo removal: A shift in identity. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:879–84. - PubMed
-
- Alster SA. Q-switched alexandrite laser treatment (755 nm) of professional and amateur tattoos. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33:69–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

