A Leap above Friedewald Formula for Calculation of Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol
- PMID: 25949053
- PMCID: PMC4411803
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2727.154780
A Leap above Friedewald Formula for Calculation of Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose was to compare the different calculated methods of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) estimation and to determine which of them correlate best with the direct method.
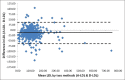
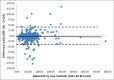
Materials and methods: The records of 480 samples for lipid profile were analyzed. Apart from the direct method, LDL-C was calculated by Friedewald low-density lipoprotein cholesterol method (F-LDL-C), modified Friedewald low-density lipoprotein cholesterol method (MF-LDL-C), and Anandaraja low-density lipoprotein cholesterol method (A-LDL-C). Paired t-test and Pearson correlation were evaluated between the different methods. Degree of agreement between the calculated methods and direct method was detected by Bland-Altman graphical plots.
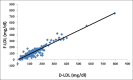
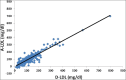
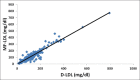
Results: A strong correlation was found between all calculated LDL-C methods and direct low-density lipoprotein cholesterol method (D-LDL-C) assay, that is, F-LDL-C versus D-LDL-C = 0.94; A-LDL-C versus D-LDL-C = 0.93 and MF-LDL-C versus D-LDL-C = 0.95. No statistically significant difference was found between D-LDL-C and MF-LDL-C. Bland-Altman plot for MF-LDL-C showed minimal negative bias.
Conclusions: The study pointed out that MF-LDL-C correlated maximally with D-LDL-C estimation at all levels of triglycerides and MF-LDL-C can be used in place of D-LDL-C when the direct method cannot be afforded.
Keywords: Anandaraja; Friedewald; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; modified Friedewald.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Geneva: WHO; 2011. World Health Organization. Global Atlas on CVD Prevention and Control.
-
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB, Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation. 2004;110:227–39. - PubMed
-
- Bachorik PS, Ross JW. National Cholesterol Education Program recommendations for measurement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: Executive summary. The National Cholesterol Education Program Working Group on Lipoprotein Measurement. Clin Chem. 1995;41:1414–20. - PubMed
-
- Nauck M, Warnick GR, Rifai N. Methods for measurement of LDL-cholesterol: A critical assessment of direct measurement by homogeneous assays versus calculation. Clin Chem. 2002;48:236–54. - PubMed
-
- Kamal AH, Hossain M, Chowdhury S, Mahmud NU. A comparison of calculated with direct measurement of low density lipoprotein cholesterol level. Journal of Chittagong Medical College Teacher's Association. 2009;20:19–23.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

