Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy plus bevacizumab after response to bevacizumab plus irinotecan as a rescue treatment for high-grade gliomas
- PMID: 25949228
- PMCID: PMC4418580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2015.01.004
Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy plus bevacizumab after response to bevacizumab plus irinotecan as a rescue treatment for high-grade gliomas
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the possibility of implementing a new scheme of rescue treatment after relapse or progression of high-grade glioma (HGG) treated at the first-line with bevacizumab and irinotecan (BVZ+CPT11), evaluating the response and toxicity of associating BVZ and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (BVZ+FSRT).
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analysed data from 59 patients with relapse of HGG. Nine patients with HGG relapse after treatment using the Stupp protocol that were treated with BVZ+CPT11 for progression between July 2007 and August 2012, after which the response was assessed according to the Revised Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria. BVZ was administered at a dose of 10 mg/kg and FSRT up to a prescribed dose of 30 Gy, 500 cGy per fraction, three days a week. The median follow-up was 38 months.
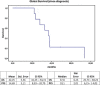
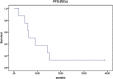
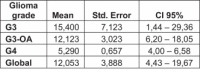
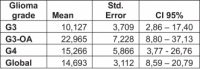
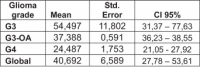
Results: The treatment was well-tolerated by all patients. The response after nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 3-6 months was progression in two patients, stable disease in four, and three patients had a partial response. The median overall survival (OS) from diagnosis until death or the last control was 36.8 months. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 10.8 months. The results from tumour sub-group analysis indicated that the PFS was not statistically significant although it seemed that it was higher in grade-III. The OS was higher in grade-III gliomas.
Conclusions: The combination of BVZ+FSRT as a second-line HGG relapse rescue treatment is well-tolerated and seems to offer promising results. We believe that multi-centre prospective studies are needed to determine the long-term efficacy and toxicity of this therapeutic approach.
Keywords: ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; BVZ, bevacizumab; Bevacizumab; CAT, computed axial tomography; CI, confidence interval; CPT11, irinotecan; CR, complete response; CTCAE, common terminology criteria for adverse events; FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; FSRT, fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy; Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy; GTV, gross tumour volume; HGG, high-grade glioma; HR, hazard ratio; High-grade glioma; KPS, Karnofsky Performance Scale; MGMT, O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NA, not applicable; OS, overall survival; PD, progressive disease; PET, positron emission tomography; PFS, progression-free survival; PR, partial response; PTV, planning target volume; RANO, revised Assessment in Neuro-Oncology; Rescue treatment; SD, stable disease; SEOM, Sociedad Española de Oncología Médica; SRS, stereotactic radiosurgery; TMZ, temozolomide; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R., Hegi M.E., Mason W.P. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolamide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomized phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. - PubMed
-
- Cabrera A.R., Cuneo K.C., Desjardins A. Concurrent stereotactic radiosurgery and bevacizumab in recurrent malignant gliomas: a prospective trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;86(5):873–879. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro L.Q., Beal K., Goenka A. Patterns of failure after concurrent bevacizumab and hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for recurrent high-grade glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85(3):636–642. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

