Progressive bevacizumab-associated renal thrombotic microangiopathy
- PMID: 25949282
- PMCID: PMC4421476
- DOI: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfn168
Progressive bevacizumab-associated renal thrombotic microangiopathy
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is integral to the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier. Bevacizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against VEGF with expanding clinical applications for metastatic solid tumours. We describe a case of a 61-year-old female with ovarian cancer and baseline chronic kidney disease who received three doses of bevacizumab and subsequently developed progressive renal clearance dysfunction and nephrotic range proteinuria. A renal biopsy was performed 4 months after drug discontinuation and was consistent with TMA. At baseline, prior to bevacizumab exposure, her estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 44 mL/min/1.73 m(2) and she had no proteinuria. At the completion of therapy, eGFR was 27 mL/min/1.73 m(2) with 1+ proteinuria on urinalysis. Her renal failure and proteinuria continued to progress 5 months after discontinuation of bevacizumab therapy, at which time eGFR was 11 mL/min/1.73 m(2) and proteinuria was 5.5 g/24 h. Non-remitting TMA after bevacizumab therapy in patients with pre-existing chronic kidney disease has not been previously reported. Further studies are needed to assess the safety of this drug in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: VEGF inhibitor; bevacizumab; renal failure; thrombotic microangiopathy.
Figures
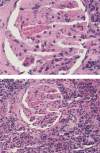
References
-
- Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Novotny W. Bevacizumab (Avastin), a humanized anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody for cancer therapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;333:328–335. - PubMed
-
- Midgley R, Kerr D. Bevacizumab—current status and future directions. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:999–1004. - PubMed
-
- Izzedine H, Rixe O, Billemont B, et al. Angiogenesis inhibitor therapies: focus on kidney toxicity and hypertension. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;50:203–218. - PubMed
-
- Frangié C, Lefaucheur C, Jacquot C, et al. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy caused by anti-VEGF antibody treatment for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:177–178. - PubMed
-
- Roncone D, Satoskar A, Nadasdy T, et al. Proteinuria in a patient receiving anti-VEGF therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007;3:287–293. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
