Polycythaemia treated with nephrectomy
- PMID: 25949492
- PMCID: PMC4421443
- DOI: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfr066
Polycythaemia treated with nephrectomy
Abstract
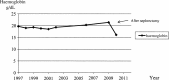
Unilateral renal cystic disease (URCD) is a rare, non-familial non-progressive renal disorder not associated with cysts in other organs in contrast to autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Only 55 cases have been published in the world literature. Renal diseases are a well-recognized etiology of secondary erythrocytosis but not in URCD. We can present at case of URCD and secondary polycythaemia. Only one case with similar history has been reported, but in our case, the polycythaemia was confirmed by measuring the erythropoietin (EPO) level in the cyst fluid.
Keywords: polycythaemia; renal cyst; secondary unilateral renal cystic disease.
Figures
References
-
- Blake James B, Attar KH, Rabbani S, et al. Secondary polycythaemia associated with unilateral renal cystic disease. Int Urol Nephrol. 2007;39:955–958. - PubMed
-
- Bisceglia M, Galliani CA, Senger C, et al. Renal cystic diseases: a review. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13:26–56. - PubMed
-
- Levine E, Huntrakoon M. Unilateral renal cystic disease: CT findings. J Compt Assist Tomogr. 1989;13:273–276. - PubMed
-
- Hwang DY, Curie A, Jung GL, et al. Unilateral renal cystic disease in adults. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14:1999–2003. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Park SK, Kang SK, et al. A case of unilateral renal cystic disease. Nephrol. 2004;9:31–32. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials