Regulation of System xc(-) by Pharmacological Manipulation of Cellular Thiols
- PMID: 25949770
- PMCID: PMC4407525
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/269371
Regulation of System xc(-) by Pharmacological Manipulation of Cellular Thiols
Abstract
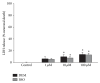
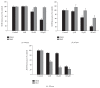
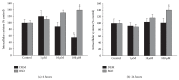
The cystine/glutamate exchanger (system xc (-)) mediates the transport of cystine into the cell in exchange for glutamate. By releasing glutamate, system xc (-) can potentially cause excitotoxicity. However, through providing cystine to the cell, it regulates the levels of cellular glutathione (GSH), the main endogenous intracellular antioxidant, and may protect cells against oxidative stress. We tested two different compounds that deplete primary cortical cultures containing both neurons and astrocytes of intracellular GSH, L-buthionine-sulfoximine (L-BSO), and diethyl maleate (DEM). Both compounds caused significant concentration and time dependent decreases in intracellular GSH levels. However; DEM caused an increase in radiolabeled cystine uptake through system xc (-), while unexpectedly BSO caused a decrease in uptake. The compounds caused similar low levels of neurotoxicity, while only BSO caused an increase in oxidative stress. The mechanism of GSH depletion by these two compounds is different, DEM directly conjugates to GSH, while BSO inhibits γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase, a key enzyme in GSH synthesis. As would be expected from these mechanisms of action, DEM caused a decrease in intracellular cysteine, while BSO increased cysteine levels. The results suggest that negative feedback by intracellular cysteine is an important regulator of system xc (-) in this culture system.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

