Cytomegalovirus, Toxoplasma gondii and Rubella Vertical Transmission Rates According to Mid-trimester Amniocentesis: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 25949782
- PMCID: PMC4410442
- DOI: 10.4103/2008-7802.154774
Cytomegalovirus, Toxoplasma gondii and Rubella Vertical Transmission Rates According to Mid-trimester Amniocentesis: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Objective: To examine vertical transmission rates of Cytomegalovirus, Toxoplasma Gondii and Rubella infections according to amniotic fluid PCR analysis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of mid-trimester amniocenteses performed in in pregnancies with diagnosed maternal infection by Cytomegavirus (CMV), Rubella or Toxoplasma gondii during 1994-2008 was performed. Vertical transmission rates were observed according to the presence of the infectious agent's DNA in the amniotic fluid. A univariate regression model was also performed to investigate possible correlations between transmission and epidemiological parameters.
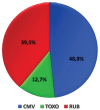
Results: Overall, 7033 amniocenteses were performed during study's period, of which 166 (2.4%) with the indication of maternal infection by CMV, Rubella or Toxoplasma. Mean maternal age was 27.4 ± 2.5 years and the mean gestational age at amniocentesis was 18.7 ± 2.5 weeks. Vertical transmission was observed in 21 cases (12.7%). Transmission rate was 17.3% in cases with infection from CMV, 9.5% from Toxoplasma gondii and 7.8% from Rubella (P = .05). Maternal age was the only parameter being significantly associated with increased risk for vertical transmission (P = .04).
Conclusions: According to our results, overall vertical transmission rate marginally exceeds 10%. CMV infection is characterized by relatively higher transplacental transmission rate, while increased maternal age appears to be associated with a higher risk for vertical transmission.
Keywords: Amniocentesis; cytomegalovirus; infection; rubella; toxoplasma; vertical transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Stegmann BJ, Carey JC. TORCH Infections. Toxoplasmosis, Other (syphilis, varicella-zoster, parvovirus B19), Rubella, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Herpes infections. Curr Womens Health Rep. 2002;2:253–8. - PubMed
-
- Bessières MH, Berrebi A, Cassaing S, Fillaux J, Cambus JP, Berry A, et al. Diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis: Prenatal and neonatal evaluation of methods used in Toulouse University Hospital and incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009;104:389–92. - PubMed
-
- Gras L, Wallon M, Pollak A, Cortina-Borja M, Evengard B, Hayde M, et al. Association between prenatal treatment and clinical manifestations of congenital toxoplasmosis in infancy: A cohort study in 13 European centres. Acta Paediatr. 2005;94:1721–31. - PubMed
-
- Villena I, Ancelle T, Delmas C, Garcia P, Brezin AP, Thulliez P, et al. Congenital toxoplasmosis in France in 2007: First results from a national surveillance system. Euro Surveill. 2010;15 pii: 19600. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources