Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO)-reactive T cells differ in their functional characteristics in health and cancer
- PMID: 25949861
- PMCID: PMC4368150
- DOI: 10.4161/21624011.2014.968480
Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO)-reactive T cells differ in their functional characteristics in health and cancer
Abstract
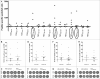
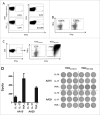
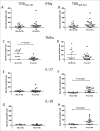
Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) physiologically regulates systemic tryptophan levels in the liver. However, numerous studies have linked cancer with activation of local and systemic tryptophan metabolism. Indeed, similar to other heme dioxygenases TDO is constitutively expressed in many cancers. In the present study, we detected the presence of both CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell reactivity toward TDO in peripheral blood of patients with malignant melanoma (MM) or breast cancer (BC) as well as healthy subjects. However, TDO-reactive CD4+ T cells constituted distinct functional phenotypes in health and disease. In healthy subjects these cells predominately comprised interferon (IFN)γ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α producing Th1 cells, while in cancer patients TDO-reactive CD4+ T-cells were more differentiated with release of not only IFNγ and TNFα, but also interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-10 in response to TDO-derived MHC-class II restricted peptides. Hence, in healthy donors (HD) a Th1 helper response was predominant, whereas in cancer patients CD4+ T-cell responses were skewed toward a regulatory T cell (Treg) response. Furthermore, MM patients hosting a TDO-specific IL-17 response showed a trend toward an improved overall survival (OS) compared to MM patients with IL-10 producing, TDO-reactive CD4+ T cells. For further characterization, we isolated and expanded both CD8+ and CD4+ TDO-reactive T cells in vitro. TDO-reactive CD8+ T cells were able to kill HLA-matched tumor cells of different origin. Interestingly, the processed and presented TDO-derived epitopes varied between different cancer cells. With respect to CD4+ TDO-reactive T cells, in vitro expanded T-cell cultures comprised a Th1 and/or a Treg phenotype. In summary, our data demonstrate that the immune modulating enzyme TDO is a target for CD8+ and CD4+ T cell responses both in healthy subjects as well as patients with cancer; notably, however, the functional phenotype of these T-cell responses differ depending on the respective conditions of the host.
Keywords: T cells; TDO; Th17; Tregs; immune regulation.
Figures



References
-
- Muller A, Heseler K, Schmidt SK, Spekker K, Mackenzie CR, Daubener W. The missing link between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediated antibacterial and immunoregulatory effects. J Cell Mol Med 2009; 13:1125-35; PMID:; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00542.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prendergast GC, Smith C, Thomas S, Mandik-Nayak L, Laury-Kleintop L, Metz R, Muller AJ. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase pathways of pathogenic inflammation and immune escape in cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2014; 63:721-35; PMID:; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00262-014-1549-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Kang SA, Mukherjee T, Bale S, Crane BR, Begley TP, Ealick SE. Crystal structure and mechanism of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase, a heme enzyme involved in tryptophan catabolism and in quinolinate biosynthesis. Biochemistry 2007; 46:145-55; PMID:; http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi0620095 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Batabyal D, Yeh SR. Human tryptophan dioxygenase: a comparison to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J Am Chem Soc 2007; 19:15690-701; PMID:; http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja076186k - DOI - PubMed
-
- Munn DH, Mellor AL. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tumor-induced tolerance. J Clin Invest 2007; 117:1147-54; PMID:; http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI31178 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
