Overexpression of Telomerase Protects Human and Murine Lung Epithelial Cells from Fas- and Bleomycin-Induced Apoptosis via FLIP Upregulation
- PMID: 25951185
- PMCID: PMC4423936
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126730
Overexpression of Telomerase Protects Human and Murine Lung Epithelial Cells from Fas- and Bleomycin-Induced Apoptosis via FLIP Upregulation
Abstract
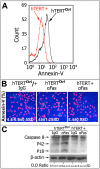
High doses of bleomycin administered to patients with lymphomas and other tumors lead to significant lung toxicity in general, and to apoptosis of epithelial cells, in particular. Apoptosis of alveolar epithelium is an important step in the pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. The Fas-FasL pathway is one of the main apoptotic pathways involved. Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein RNA-dependent DNA polymerase complex consisting of an RNA template and a catalytic protein, telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT). Telomerase also possess extra-telomeric roles, including modulation of transcription of anti-apoptotic genes, differentiation signals, and more. We hypothesized that telomerase overexpression affects Fas-induced epithelial cell apoptosis by an extra-telomeric role such as regulation of anti-apoptotic genes, specifically FLICE-like inhibitory protein (FLIP). Telomerase in mouse (MLE) and human (A549) lung epithelial cell lines was upregulated by transient transfection using cDNA hTERT expression vector. Telomerase activity was detected using a real-time PCR-based system. Bleomycin, and bleomycin-induced Fas-mediated apoptosis following treatment with anti-Fas activating mAb or control IgG, were assessed by Annexin V staining, FACS analysis, and confocal microscopy; caspase cleavage by Western blot; FLIP or Fas molecule detection by Western blot and flow cytometry. hTERT transfection of lung epithelial cells resulted in a 100% increase in their telomerase activity. Fas-induced lung epithelial cell apoptosis was significantly reduced in hTERT-transfected cells compared to controls in all experiments. Lung epithelial cells with increased telomerase activity had higher levels of FLIP expression but membrane Fas expression was unchanged. Upregulation of hTERT+ in human lung epithelial cells and subsequent downregulation of FLIP by shFLIP-RNA annulled hTERT-mediated resistance to apoptosis. Telomerase-mediated FLIP overexpression may be a novel mechanism to confer protection from apoptosis in bleomycin-exposed human lung epithelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
IL-10 protects mouse intestinal epithelial cells from Fas-induced apoptosis via modulating Fas expression and altering caspase-8 and FLIP expression.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 Nov;291(5):G820-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00438.2005. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17030898
-
Rapid up-regulation of c-FLIP expression by BCR signaling through the PI3K/Akt pathway inhibits simultaneously induced Fas-mediated apoptosis in murine B lymphocytes.Immunol Lett. 2007 Mar 15;109(1):36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2006.12.009. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Immunol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17275920
-
Inhibition of CD95 apoptotic signaling by interferon-gamma in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes is associated with increased expression of FLICE inhibitory protein.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Feb;50(2):498-506. doi: 10.1002/art.20008. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 14872492
-
Bleomycin and its role in inducing apoptosis and senescence in lung cells - modulating effects of caveolin-1.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009 May;9(3):341-53. doi: 10.2174/156800909788166501. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19442053 Review.
-
Regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling by c-FLIP: towards targeting cancer networks.Trends Cancer. 2022 Mar;8(3):190-209. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2021.12.002. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Trends Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34973957 Review.
Cited by
-
TPP1 Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of Transplanted Aged Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Infarcted Hearts via the MRE11/AKT Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 29;8:588023. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.588023. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195247 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Telomerase and Telomeres in Interstitial Lung Diseases: From Molecules to Clinical Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 19;20(12):2996. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122996. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31248154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

