Alterations in perivascular sympathetic and nitrergic innervation function induced by late pregnancy in rat mesenteric arteries
- PMID: 25951331
- PMCID: PMC4423985
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126017
Alterations in perivascular sympathetic and nitrergic innervation function induced by late pregnancy in rat mesenteric arteries
Abstract
Background and purpose: We investigated whether pregnancy was associated with changed function in components of perivascular mesenteric innervation and the mechanism/s involved.
Experimental approach: We used superior mesenteric arteries from female Sprague-Dawley rats divided into two groups: control rats (in oestrous phase) and pregnant rats (20 days of pregnancy). Modifications in the vasoconstrictor response to electrical field stimulation (EFS) were analysed in the presence/absence of phentolamine (alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist) or L-NAME (nitric oxide synthase-NOS- non-specific inhibitor). Vasomotor responses to noradrenaline (NA), and to NO donor DEA-NO were studied, NA and NO release measured and neuronal NOS (nNOS) expression/activation analysed.
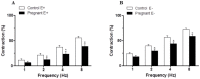
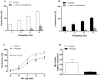
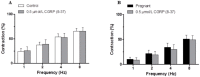
Key results: EFS induced a lower frequency-dependent contraction in pregnant than in control rats. Phentolamine decreased EFS-induced vasoconstriction in segments from both experimental groups, but to a greater extent in control rats. EFS-induced vasoconstriction was increased by L-NAME in arteries from both experimental groups. This increase was greater in segments from pregnant rats. Pregnancy decreased NA release while increasing NO release. nNOS expression was not modified but nNOS activation was increased by pregnancy. Pregnancy decreased NA-induced vasoconstriction response and did not modify DEA-NO-induced vasodilation response.
Conclusions and implications: Neural control of mesenteric vasomotor tone was altered by pregnancy. Diminished sympathetic and enhanced nitrergic components both contributed to the decreased vasoconstriction response to EFS during pregnancy. All these changes indicate the selective participation of sympathetic and nitrergic innervations in vascular adaptations produced during pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Alterations in perivascular innervation function in mesenteric arteries from offspring of diabetic rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;172(19):4699-713. doi: 10.1111/bph.13244. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26177571 Free PMC article.
-
Fenofibrate increases neuronal vasoconstrictor response in mesenteric arteries from diabetic rats: role of noradrenaline, neuronal nitric oxide and calcitonin gene-related peptide.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;666(1-3):142-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.03.056. Epub 2011 May 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21620828
-
Breast feeding increases vasoconstriction induced by electrical field stimulation in rat mesenteric artery. Role of neuronal nitric oxide and ATP.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053802. Epub 2013 Jan 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342008 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrergic perivascular innervation in health and diseases: Focus on vascular tone regulation.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020 Sep;230(1):e13484. doi: 10.1111/apha.13484. Epub 2020 May 16. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020. PMID: 32336027 Review.
-
Sympathetic modulation of nitrergic neurogenic vasodilation in cerebral arteries.Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;88(1):26-31. doi: 10.1254/jjp.88.26. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11859855 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteolytic degradation of regulator of G protein signaling 2 facilitates temporal regulation of Gq/11 signaling and vascular contraction.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 24;292(47):19266-19278. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.797134. Epub 2017 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28974581 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G Protein Signaling 2 Facilitates Uterine Artery Adaptation During Pregnancy in Mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 May 7;8(9):e010917. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010917. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31030617 Free PMC article.
-
A Blunted Sympathetic Function and an Enhanced Nitrergic Activity Contribute to Reduce Mesenteric Resistance in Hyperthyroidism.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):570. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020570. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430047 Free PMC article.
-
Decompensated liver cirrhosis and neural regulation of mesenteric vascular tone in rats: role of sympathetic, nitrergic and sensory innervations.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 3;6:31076. doi: 10.1038/srep31076. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27484028 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effect of a Multistrain Synbiotic Prodefen® Plus on the Systemic and Vascular Alterations Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Rats: The Role of the Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase and Protein Kinase A.Nutrients. 2020 Jan 1;12(1):117. doi: 10.3390/nu12010117. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 31906276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parent A, Schiffrin EL, St-Louis J. Role of the endothelium in adrenergic responses of mesenteric artery rings of pregnant rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990; 163: 229–234. - PubMed
-
- Crandall ME, Keve TM, McLaughlin MK. Characterization of norepinephrine sensitivity in the maternal splanchnic circulation during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990; 162: 1296–1301. - PubMed
-
- Learmont JG, Cockell AP, Knock GA, Poston L. Myogenic and flow-mediated responses in isolated mesenteric small arteries from pregnant and nonpregnant rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1996; 174: 1631–1636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

