Impact of QTL properties on the accuracy of multi-breed genomic prediction
- PMID: 25951906
- PMCID: PMC4424523
- DOI: 10.1186/s12711-015-0124-6
Impact of QTL properties on the accuracy of multi-breed genomic prediction
Abstract
Background: Although simulation studies show that combining multiple breeds in one reference population increases accuracy of genomic prediction, this is not always confirmed in empirical studies. This discrepancy might be due to the assumptions on quantitative trait loci (QTL) properties applied in simulation studies, including number of QTL, spectrum of QTL allele frequencies across breeds, and distribution of allele substitution effects. We investigated the effects of QTL properties and of including a random across- and within-breed animal effect in a genomic best linear unbiased prediction (GBLUP) model on accuracy of multi-breed genomic prediction using genotypes of Holstein-Friesian and Jersey cows.
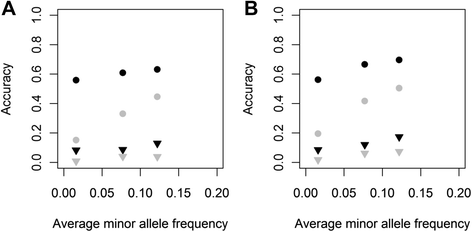
Methods: Genotypes of three classes of variants obtained from whole-genome sequence data, with moderately low, very low or extremely low average minor allele frequencies (MAF), were imputed in 3000 Holstein-Friesian and 3000 Jersey cows that had real high-density genotypes. Phenotypes of traits controlled by QTL with different properties were simulated by sampling 100 or 1000 QTL from one class of variants and their allele substitution effects either randomly from a gamma distribution, or computed such that each QTL explained the same variance, i.e. rare alleles had a large effect. Genomic breeding values for 1000 selection candidates per breed were estimated using GBLUP modelsincluding a random across- and a within-breed animal effect.
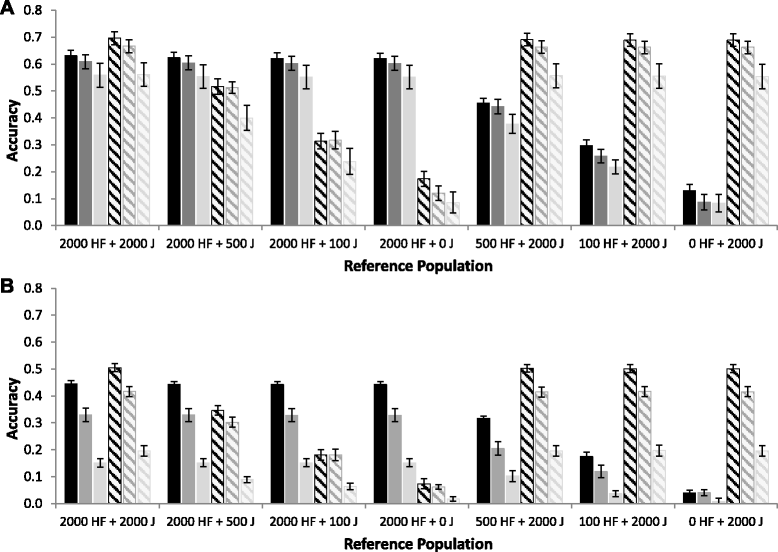
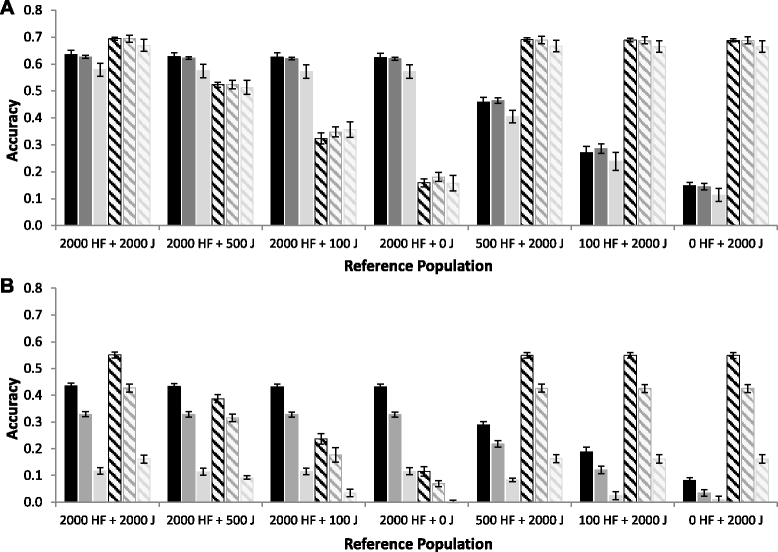
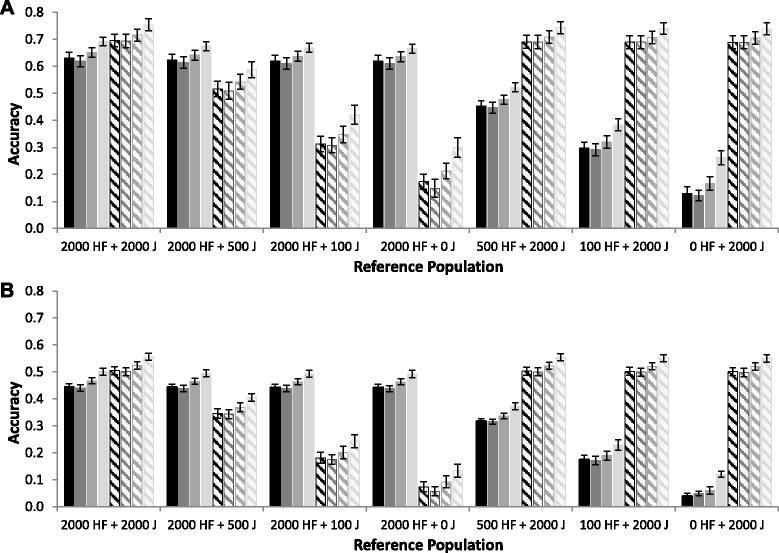
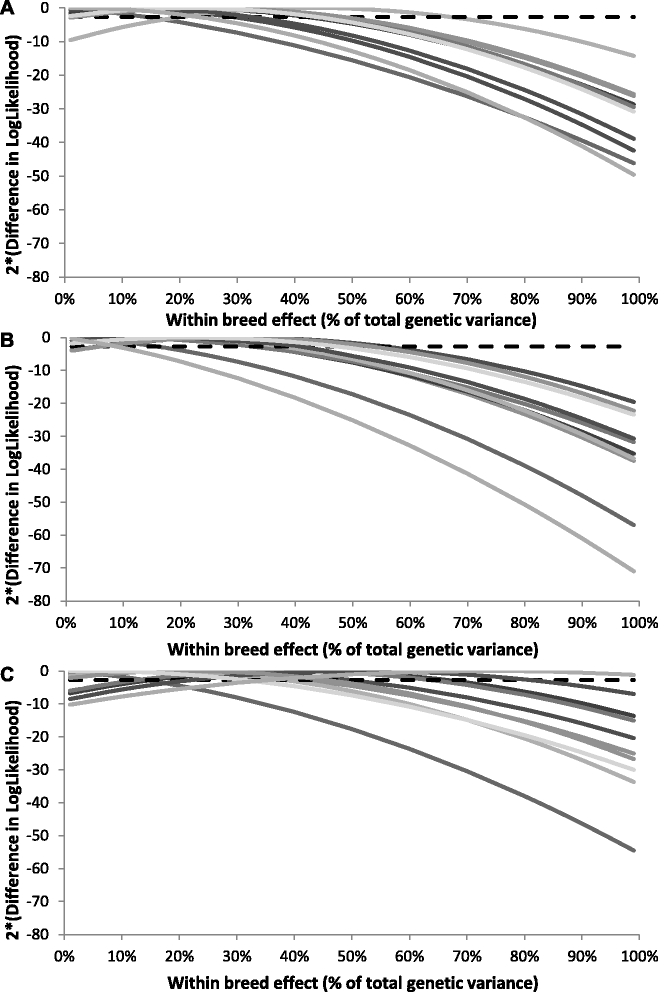
Results: For all three classes of QTL allele frequency spectra, accuracies of genomic prediction were not affected by the addition of 2000 individuals of the other breed to a reference population of the same breed as the selection candidates. Accuracies of both single- and multi-breed genomic prediction decreased as MAF of QTL decreased, especially when rare alleles had a large effect. Accuracies of genomic prediction were similar for the models with and without a random within-breed animal effect, probably because of insufficient power to separate across- and within-breed animal effects.
Conclusions: Accuracy of both single- and multi-breed genomic prediction depends on the properties of the QTL that underlie the trait. As QTL MAF decreased, accuracy decreased, especially when rare alleles had a large effect. This demonstrates that QTL properties are key parameters that determine the accuracy of genomic prediction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Empirical and deterministic accuracies of across-population genomic prediction.Genet Sel Evol. 2015 Feb 6;47(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12711-014-0086-0. Genet Sel Evol. 2015. PMID: 25885467 Free PMC article.
-
Improved precision of QTL mapping using a nonlinear Bayesian method in a multi-breed population leads to greater accuracy of across-breed genomic predictions.Genet Sel Evol. 2015 Apr 17;47(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12711-014-0074-4. Genet Sel Evol. 2015. PMID: 25887988 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of QTL minor allele frequency on genomic evaluation using real genotype data and simulated phenotypes in Japanese Black cattle.BMC Genet. 2015 Nov 19;16:134. doi: 10.1186/s12863-015-0287-8. BMC Genet. 2015. PMID: 26586567 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic prediction in animals and plants: simulation of data, validation, reporting, and benchmarking.Genetics. 2013 Feb;193(2):347-65. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.147983. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23222650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of measures of correctness of genotype imputation in the context of genomic prediction: a review of livestock applications.Animal. 2014 Nov;8(11):1743-53. doi: 10.1017/S1751731114001803. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Animal. 2014. PMID: 25045914 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic-inferred cross-selection methods for multi-trait improvement in a recurrent selection breeding program.Plant Methods. 2024 Sep 2;20(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13007-024-01258-4. Plant Methods. 2024. PMID: 39218896 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence variants selected from a multi-breed GWAS can improve the reliability of genomic predictions in dairy cattle.Genet Sel Evol. 2016 Nov 4;48(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0259-0. Genet Sel Evol. 2016. PMID: 27809758 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype Imputation in Winter Wheat Using First-Generation Haplotype Map SNPs Improves Genome-Wide Association Mapping and Genomic Prediction of Traits.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Jan 9;9(1):125-133. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200664. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30420469 Free PMC article.
-
An Equation to Predict the Accuracy of Genomic Values by Combining Data from Multiple Traits, Populations, or Environments.Genetics. 2016 Feb;202(2):799-823. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.183269. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26637542 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical Evaluation of Multi-Breed Genomic Prediction in Chinese Indigenous Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2019 Oct 11;9(10):789. doi: 10.3390/ani9100789. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31614691 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

