P450s and UGTs: Key Players in the Structural Diversity of Triterpenoid Saponins
- PMID: 25951908
- PMCID: PMC7107090
- DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcv062
P450s and UGTs: Key Players in the Structural Diversity of Triterpenoid Saponins
Abstract
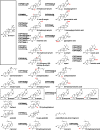
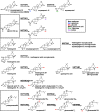
The recent spread of next-generation sequencing techniques has facilitated transcriptome analyses of non-model plants. As a result, many of the genes encoding enzymes related to the production of specialized metabolites have been identified. Compounds derived from 2,3-oxidosqualene (the common precursor of sterols, steroids and triterpenoids), a linear compound of 30 carbon atoms produced through the mevalonate pathway, are called triterpenes. These include essential sterols, which are structural components of biomembranes; steroids such as the plant hormones, brassinolides and the toxin in potatoes, solanine; as well as the structurally diverse triterpenoids. Triterpenoids containing one or more sugar moieties attached to triterpenoid aglycones are called triterpenoid saponins. Triterpenoid saponins have been shown to have various medicinal properties, such as anti-inflammatory, anticancerogenic and antiviral effects. This review summarizes the recent progress in gene discovery and elucidates the biochemical functions of biosynthetic enzymes in triterpenoid saponin biosynthesis. Special focus is placed on key players in generating the structural diversity of triterpenoid saponins, cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (P450s) and the UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases (UGTs). Perspectives on further gene discovery and the use of biosynthetic genes for the microbial production of plant-derived triterpenoid saponins are also discussed.
Keywords: Biosynthesis; Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; Oxidosqualene cyclase; Plant specialized metabolites; Triterpenoid saponin; UDP-dependent glycosyltransferase.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Japanese Society of Plant Physiologists. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Achnine L., Huhman D.V., Farag M.A., Sumner L.W., Blount J.W., Dixon R.A. (2005) Genomics-based selection and functional characterization of triterpene glycosyltransferases from the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant J. 41: 875–887. - PubMed
-
- Augustin J.M., Kuzina V., Andersen S.B., Bak S. (2011) Molecular activities, biosynthesis and evolution of triterpenoid saponins. Phytochemistry 72: 435–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

