Activating PIK3CA Mutations Induce an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)/Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK) Paracrine Signaling Axis in Basal-like Breast Cancer
- PMID: 25953087
- PMCID: PMC4587316
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M115.049783
Activating PIK3CA Mutations Induce an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)/Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK) Paracrine Signaling Axis in Basal-like Breast Cancer
Abstract
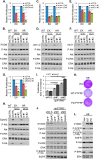
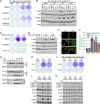
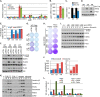
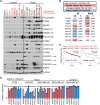
Mutations in PIK3CA, the gene encoding the p110α catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) have been shown to transform human mammary epithelial cells (MECs). These mutations are present in all breast cancer subtypes, including basal-like breast cancer (BLBC). Using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), we identified 72 protein expression changes in human basal-like MECs with knock-in E545K or H1047R PIK3CA mutations versus isogenic MECs with wild-type PIK3CA. Several of these were secreted proteins, cell surface receptors or ECM interacting molecules and were required for growth of PIK3CA mutant cells as well as adjacent cells with wild-type PIK3CA. The proteins identified by MS were enriched among human BLBC cell lines and pointed to a PI3K-dependent amphiregulin/EGFR/ERK signaling axis that is activated in BLBC. Proteins induced by PIK3CA mutations correlated with EGFR signaling and reduced relapse-free survival in BLBC. Treatment with EGFR inhibitors reduced growth of PIK3CA mutant BLBC cell lines and murine mammary tumors driven by a PIK3CA mutant transgene, all together suggesting that PIK3CA mutations promote tumor growth in part by inducing protein changes that activate EGFR.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Conditional loss of ErbB3 delays mammary gland hyperplasia induced by mutant PIK3CA without affecting mammary tumor latency, gene expression, or signaling.Cancer Res. 2013 Jul 1;73(13):4075-85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4579. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23633485 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of STAT3, β-catenin, and IGF-1R sensitize mouse PIK3CA-mutant breast cancer to PI3K inhibitors.Mol Oncol. 2017 May;11(5):552-566. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12053. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Mol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28296140 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated molecular pathway analysis informs a synergistic combination therapy targeting PTEN/PI3K and EGFR pathways for basal-like breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 2;16:587. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2609-2. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27484095 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation distributions and clinical correlations of PIK3CA gene mutations in breast cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7033-45. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4924-2. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26921096 Review.
-
PIK3CA mutations matter for cancer in dogs.Res Vet Sci. 2020 Dec;133:39-41. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Res Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32932196 Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of USF1 Inhibits the Vasculogenic Mimicry of Glioma Cells via Stimulating SNHG16/miR-212-3p and linc00667/miR-429 Axis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Mar 1;14:465-482. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.12.017. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. Retraction in: Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 May 10;28:587. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.05.001. PMID: 30743215 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Potentiating Therapeutic Effects of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jun 18;14(6):589. doi: 10.3390/ph14060589. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amphiregulin Exerts Proangiogenic Effects in Developing Murine Lungs.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 8;13(1):78. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010078. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247502 Free PMC article.
-
CD49f and CD146: A Possible Crosstalk Modulates Adipogenic Differentiation Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Cells. 2023 Dec 27;13(1):55. doi: 10.3390/cells13010055. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201259 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant PIK3CA Induces EMT in a Cell Type Specific Manner.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 12;11(12):e0167064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167064. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27941987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Debnath J., Brugge J. S. (2005) Modeling glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 675–688 - PubMed
-
- Gustin J. P., Karakas B., Weiss M. B., Abukhdeir A. M., Lauring J., Garay J. P., Cosgrove D., Tamaki A., Konishi H., Konishi Y., Mohseni M., Wang G., Rosen D. M., Denmeade S. R., Higgins M. J., Vitolo M. I., Bachman K. E., Park B. H. (2009) Knockin of mutant PIK3CA activates multiple oncogenic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 2835–2840 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neve R. M., Chin K., Fridlyand J., Yeh J., Baehner F. L., Fevr T., Clark L., Bayani N., Coppe J. P., Tong F., Speed T., Spellman P. T., DeVries S., Lapuk A., Wang N. J., Kuo W. L., Stilwell J. L., Pinkel D., Albertson D. G., Waldman F. M., McCormick F., Dickson R. B., Johnson M. D., Lippman M., Ethier S., Gazdar A., Gray J. W. (2006) A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 10, 515–527 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang H., Qian W. J., Mottaz H. M., Clauss T. R., Anderson D. J., Moore R. J., Camp D. G., 2nd, Khan A. H., Sforza D. M., Pallavicini M., Smith D. J., Smith R. D. (2005) Development and evaluation of a micro- and nanoscale proteomic sample preparation method. J. Proteome Res. 4, 2397–2403 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

