Functional Uncoupling NMDAR NR2A Subunit from PSD-95 in the Prefrontal Cortex: Effects on Behavioral Dysfunction and Parvalbumin Loss after Early-Life Stress
- PMID: 25953359
- PMCID: PMC4864660
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2015.134
Functional Uncoupling NMDAR NR2A Subunit from PSD-95 in the Prefrontal Cortex: Effects on Behavioral Dysfunction and Parvalbumin Loss after Early-Life Stress
Erratum in
-
Functional Uncoupling NMDAR NR2A Subunit from PSD-95 in the Prefrontal Cortex: Effects on Behavioral Dysfunction and Parvalbumin Loss after Early-Life Stress.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Mar;41(4):1188. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.334. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26856605 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
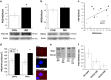
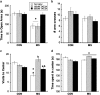
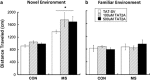
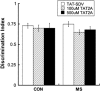
Exposure to early-life stress increases vulnerability to psychiatric disorders, including depression, schizophrenia, and anxiety. Growing evidence implicates aberrant development of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in the effects of early-life stress, which often emerge in adolescence or young adulthood. Specifically, early-life stress in the form of maternal separation (MS) in rodents has been shown to decrease parvalbumin (PVB)-positive interneurons in the adolescent PFC; however, the mechanism underpinning behavioral dysfunction and PVB loss is not yet known. We recently reported that MS causes overexpression of the NMDA subunit NR2A in the PFC of adolescent rats. Elevated PFC NR2A is also found in developmental models of schizophrenia and is correlated with behavioral deficits, acting largely through its association with the postsynaptic protein PSD-95. In addition, adolescent maturation of PVB-positive interneurons relies on NR2A-driven NMDA activity. Therefore, it is possible that the NR2A/PSD-95 signaling complex has a role in adolescent MS effects. Here, we aimed to determine whether a discrete manipulation of PFC NR2A could prevent MS effects on PFC-controlled behaviors, including cognition, anxiety, and novelty-induced hyperlocomotion, as well as PVB loss in adolescence. We intracranially infused the NR2A-specific blocking peptide TAT2A in order to uncouple NR2A from PSD-95 in the early-adolescent PFC, without antagonizing the NMDA receptor. We demonstrated that MS rats treated with TAT2A during early adolescence were protected from MS-induced PVB loss and exhibited less anxious behavior than those infused with control peptide. These data implicate NR2A-related N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor development in adolescent behavioral and neural consequences of early-life stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A lasting effect of postnatal sevoflurane anesthesia on the composition of NMDA receptor subunits in rat prefrontal cortex.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2016 Nov;54:62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27025552
-
Adolescent Stress Disrupts the Maturation of Anxiety-related Behaviors and Alters the Developmental Trajectory of the Prefrontal Cortex in a Sex- and Age-specific Manner.Neuroscience. 2018 Oct 15;390:265-277. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.08.030. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 30179643
-
Evidence for a neuroinflammatory mechanism in delayed effects of early life adversity in rats: relationship to cortical NMDA receptor expression.Brain Behav Immun. 2013 Feb;28:218-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.11.012. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Brain Behav Immun. 2013. PMID: 23207107
-
Involvement of NR1, NR2A different expression in brain regions in anxiety-like behavior of prenatally stressed offspring.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Nov 15;257:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.08.044. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 24029697 Review.
-
NR2B subunit in the prefrontal cortex: A double-edged sword for working memory function and psychiatric disorders.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Sep;56:127-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.06.022. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 26143512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal separation modifies spontaneous synaptic activity in the infralimbic cortex of stress-resilient male rats.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 9;18(11):e0294151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294151. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37943747 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Generational Transmission of Early Life Stress Effects on HPA Regulators and Bdnf Are Mediated by Sex, Lineage, and Upbringing.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 May 9;13:101. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00101. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31143105 Free PMC article.
-
Voluntary Exercise During Adolescence Mitigated Negative the Effects of Maternal Separation Stress on the Depressive-Like Behaviors of Adult Male Rats: Role of NMDA Receptors.Neurochem Res. 2018 May;43(5):1067-1074. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2519-6. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29616445
-
Activation of GPR55 Ameliorates Maternal Separation-Induced Learning and Memory Deficits by Augmenting 5-HT Synthesis in the Dorsal Raphe Nucleus of Juvenile Mice.ACS Omega. 2024 May 7;9(20):21838-21850. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08934. eCollection 2024 May 21. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38799363 Free PMC article.
-
Circuit- and laminar-specific regulation of medial prefrontal neurons by chronic stress.Cell Biosci. 2023 May 18;13(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01050-2. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37208769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarts M, Liu Y, Liu L, Besshoh S, Arundine M, Gurd JW et al (2002). Treatment of ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor- PSD-95 protein interactions. Science 298: 846–850. - PubMed
-
- Agid O, Shapira B, Zislin J, Ritsner M, Hanin B, Murad H et al (1999). Environment and vulnerability to major psychiatric illness: a case control study of early parental loss in major depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 4: 163–172. - PubMed
-
- Aisa B, Tordera R, Lasheras B, Del Rio J, Ramirez MJ (2007). Cognitive impairment associated to HPA axis hyperactivity after maternal separation in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32: 256–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

