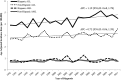
Rising rates of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Hispanic children: trends in incidence from 1992 to 2011
- PMID: 25953979
- PMCID: PMC4424421
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-03-634006
Rising rates of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Hispanic children: trends in incidence from 1992 to 2011
Figures
References
-
- Howlader N, Noone A, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2011. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2014.
-
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. The Health Consequences of Smoking - 50 Years of Progress. A report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2014.
-
- Caetano R, Vaeth PA, Chartier KG, Mills BA. Epidemiology of drinking, alcohol use disorders, and related problems in US ethnic minority groups. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;125:629–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources