A balance between TFPI and thrombin-mediated platelet activation is required for murine embryonic development
- PMID: 25954015
- PMCID: PMC4481595
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-03-633958
A balance between TFPI and thrombin-mediated platelet activation is required for murine embryonic development
Abstract
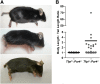
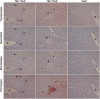
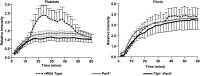
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is a critical anticoagulant protein present in endothelium and platelets. Mice lacking TFPI (Tfpi(-/-)) die in utero from disseminated intravascular coagulation. They are rescued by concomitant tissue factor (TF) deficiency, demonstrating that TFPI modulates TF function in vivo. Recent studies have found TFPI inhibits prothrombinase activity during the initiation of coagulation and limits platelet accumulation during thrombus formation, implicating TFPI in modulating platelet procoagulant activity. To examine whether altered platelet function would compensate for the lack of TFPI and rescue TFPI-null embryonic lethality, Tfpi(+/-) mice lacking the platelet thrombin receptor, protease activated receptor 4 (PAR4; Par4(-/-)), or its coreceptor, PAR3, were mated. PAR3 deficiency did not rescue Tfpi(-/-) embryos, but >40% of expected Tfpi(-/-):Par4(-/-) offspring survived to adulthood. Adult Tfpi(-/-):Par4(-/-) mice did not exhibit overt thrombosis. However, they had focal sterile inflammation with fibrin(ogen) deposition in the liver and elevated plasma thrombin-antithrombin complexes, indicating activation of coagulation at baseline. Tfpi(-/-):Par4(-/-) mice have platelet and fibrin accumulation similar to Par4(-/-) mice following venous electrolytic injury but were more susceptible than Par4(-/-) mice to TF-induced pulmonary embolism. In addition, ∼30% of the Tfpi(-/-):Par4(-/-) mice were born with short tails. Tfpi(-/-):Par4(-/-) mice are the first adult mice described that lack TFPI with unaltered TF. They demonstrate that TFPI physiologically modulates thrombin-dependent platelet activation in a manner that is required for successful embryonic development and identify a role for TFPI in dampening intravascular procoagulant stimuli that lead to thrombin generation, even in the absence of thrombin-mediated platelet activation.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Platelet tissue factor pathway inhibitor-α dampens cardiac thrombosis and associated fibrosis in mice.J Thromb Haemost. 2023 Mar;21(3):639-651. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2022.11.034. Epub 2022 Dec 22. J Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 36696221 Free PMC article.
-
Par4 is required for platelet thrombus propagation but not fibrin generation in a mouse model of thrombosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 2;104(1):288-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610188104. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17190826 Free PMC article.
-
Redundancy and interaction of thrombin- and collagen-mediated platelet activation in tail bleeding and carotid thrombosis in mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Dec;34(12):2563-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304244. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25278288 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet tissue factor pathway inhibitor modulates intravascular coagulation.Thromb Res. 2012 May;129 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S21-2. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2012.02.023. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Thromb Res. 2012. PMID: 22425319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor gene disruption.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998 Mar;9 Suppl 1:S89-92. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998. PMID: 9819035 Review.
Cited by
-
A combined deficiency of tissue factor and PAR-4 is associated with fatal pulmonary hemorrhage in mice.Thromb Res. 2016 Oct;146:46-50. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2016.08.023. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Thromb Res. 2016. PMID: 27586081 Free PMC article.
-
Correlates of plasma and platelet tissue factor pathway inhibitor, factor V, and Protein S.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2018 Jan;2(1):93-104. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12058. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29354797 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of TFPIα to the hemostatic response to injury in mice.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Sep;19(9):2182-2192. doi: 10.1111/jth.15430. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 34160126 Free PMC article.
-
Novel venous thromboembolism mouse model to evaluate the role of complete and partial factor XIII deficiency in pulmonary embolism risk.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Dec;19(12):2997-3007. doi: 10.1111/jth.15510. Epub 2021 Sep 6. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 34431201 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Thrombin Generation in Animal Plasma: Sensitivity to Human Factor XIa and Tissue Factor.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 18;24(16):12920. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612920. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Girard TJ, Warren LA, Novotny WF, et al. Functional significance of the Kunitz-type inhibitory domains of lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Nature. 1989;338(6215):518–520. - PubMed
-
- Broze GJ, Jr, Warren LA, Novotny WF, Higuchi DA, Girard JJ, Miletich JP. The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action. Blood. 1988;71(2):335–343. - PubMed
-
- Huang ZF, Higuchi D, Lasky N, Broze GJ., Jr Tissue factor pathway inhibitor gene disruption produces intrauterine lethality in mice. Blood. 1997;90(3):944–951. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

