Time dynamics of the Bacillus cereus exoproteome are shaped by cellular oxidation
- PMID: 25954265
- PMCID: PMC4406070
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00342
Time dynamics of the Bacillus cereus exoproteome are shaped by cellular oxidation
Abstract
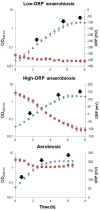
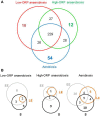
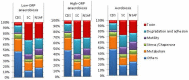
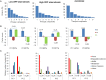
At low density, Bacillus cereus cells release a large variety of proteins into the extracellular medium when cultivated in pH-regulated, glucose-containing minimal medium, either in the presence or absence of oxygen. The majority of these exoproteins are putative virulence factors, including toxin-related proteins. Here, B. cereus exoproteome time courses were monitored by nanoLC-MS/MS under low-oxidoreduction potential (ORP) anaerobiosis, high-ORP anaerobiosis, and aerobiosis, with a specific focus on oxidative-induced post-translational modifications of methionine residues. Principal component analysis (PCA) of the exoproteome dynamics indicated that toxin-related proteins were the most representative of the exoproteome changes, both in terms of protein abundance and their methionine sulfoxide (Met(O)) content. PCA also revealed an interesting interconnection between toxin-, metabolism-, and oxidative stress-related proteins, suggesting that the abundance level of toxin-related proteins, and their Met(O) content in the B. cereus exoproteome, reflected the cellular oxidation under both aerobiosis and anaerobiosis.
Keywords: Bacillus cereus; exoproteome; methionine oxidation; shotgun proteomics; toxins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Methionine Residues in Exoproteins and Their Recycling by Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase AB Serve as an Antioxidant Strategy in Bacillus cereus.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 26;8:1342. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01342. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28798727 Free PMC article.
-
OhrRA functions as a redox-responsive system controlling toxinogenesis in Bacillus cereus.J Proteomics. 2013 Dec 6;94:527-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.10.024. Epub 2013 Oct 30. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 24184231
-
Bacillus cereus Decreases NHE and CLO Exotoxin Synthesis to Maintain Appropriate Proteome Dynamics During Growth at Low Temperature.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Oct 6;12(10):645. doi: 10.3390/toxins12100645. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33036317 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of selected factors on the survival of Bacillus cereus in the human gastrointestinal tract.Microb Pathog. 2015 May;82:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2015.03.015. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Microb Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25794697 Review.
-
Methionine sulfoxide reductases and virulence of bacterial pathogens.Future Microbiol. 2007 Dec;2(6):619-30. doi: 10.2217/17460913.2.6.619. Future Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 18041903 Review.
Cited by
-
The Diverse Functional Roles of Elongation Factor Tu (EF-Tu) in Microbial Pathogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 24;10:2351. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02351. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31708880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics identifies Bacillus cereus EntD as a pivotal protein for the production of numerous virulence factors.Front Microbiol. 2015 Oct 7;6:1004. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01004. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26500610 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome data to explore the impact of pBClin15 on Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579.Data Brief. 2016 Jul 26;8:1243-6. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.07.042. eCollection 2016 Sep. Data Brief. 2016. PMID: 27547804 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation in Bacillus cereus: From Stress to Disease.Front Microbiol. 2016 Oct 4;7:1550. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01550. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27757102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteine Proteome Reveals Response to Endogenous Oxidative Stress in Bacillus cereus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 14;22(14):7550. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147550. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299167 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

