Ectopic Germinal Centers and IgG4-Producing Plasmacytes Observed in Synovia of HLA-B27+ Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients with Advanced Hip Involvement
- PMID: 25954311
- PMCID: PMC4410505
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/316421
Ectopic Germinal Centers and IgG4-Producing Plasmacytes Observed in Synovia of HLA-B27+ Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients with Advanced Hip Involvement
Abstract
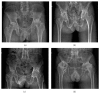
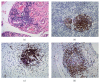
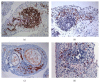
Introduction. Ectopic lymphoid neogenesis and the presence of IgG4-positive plasmacytes have been confirmed in chronic inflammatory sclerosing diseases. This study aims to investigate hip synovial tissues of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients for IgG4-positive plasma cells and ectopic lymphoid tissues with germinal centers (GCs). Methods. Synovial samples were collected from 7 AS patients who received total hip replacement and were evaluated using immunohistochemistry for the presence of CD20+ B-cells, CD3+ T-cells, CD21+ follicular dendritic cells (FDC), and CD38+ plasma cells. Furthermore, immunoglobulin G (IgG and IgG4), IgA, IgM, and complement components C3d and C4d in synovia were evaluated. Both synovial CD21+ FDCs and IgG4-producing plasmacytes were analyzed. Results. All seven patients had severe fibrosis. Massive infiltrations of lymphocytes were found in 5 out of 7 patients' synovia. Ectopic lymphoid tissues with CD21+ FDC networks and IgG4-positive plasma cells were observed coincidentally in two patients' synovia. Conclusion. The pathophysiological mechanism of AS patients' hip damage might be related to the coincidental presence of ectopic lymphoid tissue with FDCs network and IgG4-positive plasma cells identified here for the first time in AS patients' inflamed synovial tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary Docosahexaenoic Acid Prevents Silica-Induced Development of Pulmonary Ectopic Germinal Centers and Glomerulonephritis in the Lupus-Prone NZBWF1 Mouse.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 12;9:2002. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02002. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30258439 Free PMC article.
-
A morphological and immunohistochemical study of lymphoid germinal centers in synovial and lymph node tissues from rheumatoid arthritis patients with special reference to complement components and their receptors.Acta Pathol Jpn. 1989 Feb;39(2):127-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1989.tb01490.x. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1989. PMID: 2718766
-
Synovial lymphoid neogenesis does not define a specific clinical rheumatoid arthritis phenotype.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Jun;58(6):1582-9. doi: 10.1002/art.23505. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18512774
-
Ectopic germinal center formation in rheumatoid synovitis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Apr;987:140-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb06042.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12727633 Review.
-
Follicular dendritic cells and germinal centers.Int Rev Cytol. 1996;166:139-79. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62508-5. Int Rev Cytol. 1996. PMID: 8881775 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-TNF Therapy in Spondyloarthritis and Related Diseases, Impact on the Immune System and Prediction of Treatment Responses.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 19;10:382. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00382. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30941119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B Cell Involvement in the Pathogenesis of Ankylosing Spondylitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 11;22(24):13325. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413325. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD27-CD38lowCD21low B-Cells Are Increased in Axial Spondyloarthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 8;12:686273. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.686273. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34168654 Free PMC article.
-
Ankylosing spondylitis: an autoimmune or autoinflammatory disease?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Jul;17(7):387-404. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00625-y. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34113018 Review.
References
-
- Appel H., Loddenkemper C., Miossec P. Rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis—pathology of acute inflammation. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2009;27(4):S15–S19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

