Automatically Detecting Acute Myocardial Infarction Events from EHR Text: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 25954440
- PMCID: PMC4419972
Automatically Detecting Acute Myocardial Infarction Events from EHR Text: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
The Worcester Heart Attack Study (WHAS) is a population-based surveillance project examining trends in the incidence, in-hospital, and long-term survival rates of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) among residents of central Massachusetts. It provides insights into various aspects of AMI. Much of the data has been assessed manually. We are developing supervised machine learning approaches to automate this process. Since the existing WHAS data cannot be used directly for an automated system, we first annotated the AMI information in electronic health records (EHR). With strict inter-annotator agreement over 0.74 and un-strict agreement over 0.9 of Cohen's κ, we annotated 105 EHR discharge summaries (135k tokens). Subsequently, we applied the state-of-the-art supervised machine-learning model, Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) for AMI detection. We explored different approaches to overcome the data sparseness challenge and our results showed that cluster-based word features achieved the highest performance.
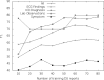
Figures
References
-
- Goldberg RJ, Gore JM, Alpert JS, Dalen JE. Recent changes in attack and survival rates of acute myocardial infarction (1975 through 1981): The worcester heart attack study. JAMA. 1986;255:2774–2779. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical