A Comparison of Data Driven-based Measures of Adherence to Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Medicaid Patients
- PMID: 25954441
- PMCID: PMC4420014
A Comparison of Data Driven-based Measures of Adherence to Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Medicaid Patients
Abstract
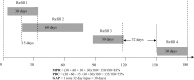
We evaluated and compared different methods for measuring adherence to Oral Antihyperglycemic Agents (OHA), based on the correlation between these measures and glycated hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) levels in Medicaid patients with Type 2 diabetes. An observational sample of 831 Medicaid patients with Type 2 diabetes who had HbA1c test results recorded between January 1, 2001 and December 31, 2005 was identified in the Indiana Network of Patient Care (INPC). OHA adherence was measured by medication possession ratio (MPR), proportion of days covered (PDC), and the number of gaps (GAP) for 3, 6, and 12-month intervals prior to the HbA1c test date. All three OHA adherence measurements showed consistent and significant correlation with HbA1c level. The 6-month PDC showed the strongest association with HbA1c levels in both unadjusted (-1.07, P<0.0001) and adjusted (-1.12, P<0.0001) models.
Figures
References
-
- Lee WC, Balu S, Cobden D, Joshi AV, Pashos CL. Prevalence and Economic Consequences of Medication Adherence in Diabetes: A Systematic Literature Review. Manag Care Interface. 2006 Jul;19(7):31–41. - PubMed
-
- Ho PM, Bryson CL, Rumsfeld JS. Medication adherence: its importance in cardiovascular outcomes. Circulation. 2009 Jun 16;119(23):3028–35. - PubMed
-
- Rubin RR. Adherence to pharmacologic therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2005;118(suppl 5A):27S–34S. - PubMed
-
- World Health Origanization Adherence to Long-term therapies: Evidence for action. 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous