Optimizing the use of thiopurines in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 25954498
- PMCID: PMC4416969
- DOI: 10.1177/2040622315579063
Optimizing the use of thiopurines in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
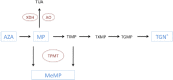
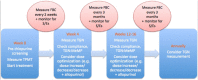
Immunomodulator drugs, of which thiopurines can be considered the backbone, are widely used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. They have been shown to be highly effective and safe; however, a significant proportion of patients are deemed to have a poor response or suffer adverse reactions. Knowing how to monitor and optimize thiopurine therapy in these scenarios is crucial to effective management. We discuss the metabolism of thiopurines, the use of enzyme/metabolite testing to guide treatment, as well as strategies to circumvent toxicity and side effects, such as allopurinol coprescription. The indications, use in pregnancy, safety profile and duration of thiopurine therapy are also discussed.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; azathioprine; drugs; gastroenterology; inflammatory bowel disease; thiopurines; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Aarbakke J., Janka-Schaub G., Elion G. (1997) Thiopurine biology and pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 18: 3–7. - PubMed
-
- Amin J., Huang B., Yoon J., Shih D. (2015) Update 2014: advances to optimize 6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine to reduce toxicity and improve efficacy in the management of IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis 21: 445–452. - PubMed
-
- Ansari A., Hassan C., Duley J., Marinaki A., Shobowale-Bakre E., Seed P., et al. (2002) Thiopurine methyltransferase activity and the use of azathioprine in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16: 1743–1750. - PubMed
-
- Ansari A., Patel N., Sanderson J., O’Donohue J., Duley J., Florin T. (2010) Low-dose azathioprine or mercaptopurine in combination with allopurinol can bypass many adverse reactions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 31: 640–647. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

