Measuring acoustic habitats
- PMID: 25954500
- PMCID: PMC4413749
- DOI: 10.1111/2041-210X.12330
Measuring acoustic habitats
Abstract
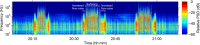
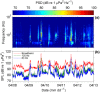
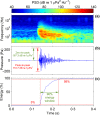
1. Many organisms depend on sound for communication, predator/prey detection and navigation. The acoustic environment can therefore play an important role in ecosystem dynamics and evolution. A growing number of studies are documenting acoustic habitats and their influences on animal development, behaviour, physiology and spatial ecology, which has led to increasing demand for passive acoustic monitoring (PAM) expertise in the life sciences. However, as yet, there has been no synthesis of data processing methods for acoustic habitat monitoring, which presents an unnecessary obstacle to would-be PAM analysts. 2. Here, we review the signal processing techniques needed to produce calibrated measurements of terrestrial and aquatic acoustic habitats. We include a supplemental tutorial and template computer codes in matlab and r, which give detailed guidance on how to produce calibrated spectrograms and statistical analyses of sound levels. Key metrics and terminology for the characterisation of biotic, abiotic and anthropogenic sound are covered, and their application to relevant monitoring scenarios is illustrated through example data sets. To inform study design and hardware selection, we also include an up-to-date overview of terrestrial and aquatic PAM instruments. 3. Monitoring of acoustic habitats at large spatiotemporal scales is becoming possible through recent advances in PAM technology. This will enhance our understanding of the role of sound in the spatial ecology of acoustically sensitive species and inform spatial planning to mitigate the rising influence of anthropogenic noise in these ecosystems. As we demonstrate in this work, progress in these areas will depend upon the application of consistent and appropriate PAM methodologies.
Keywords: acoustic ecology; ambient noise; anthropogenic noise; bioacoustics; ecoacoustics; habitat monitoring; passive acoustic monitoring; remote sensing; soundscape.
Figures


References
-
- Au WWL, Hastings MC. Principles of Marine Bioacoustics. New York: Springer; 2008.
-
- Barber JR, Crooks KR, Fristrup KM. The costs of chronic noise exposure for terrestrial organisms. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 2010;25:180–189. - PubMed
-
- Barber JR, Burdett CL, Reed SE, Warner KA, Formichella C, Crooks KR, Theobald DM, Fristrup KM. Anthropogenic noise exposure in protected natural areas: estimating the scale of ecological consequences. Journal of Landscape Ecology. 2011;26:1281–1295.
-
- Bassett C, Polagye B, Holt M, Thomson J. A vessel noise budget for Admiralty Inlet, Puget Sound, Washington (USA) The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 2012;132:3706–3719. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner MF, Fratantoni DM. Diel periodicity in both sei whale vocalization rates and the vertical migration of their copepod prey observed from ocean gliders. Limnology and Oceanography. 2008;53:2197–2209.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
