Constant-pH Molecular Dynamics Study of Kyotorphin in an Explicit Bilayer
- PMID: 25954885
- PMCID: PMC4423061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.03.052
Constant-pH Molecular Dynamics Study of Kyotorphin in an Explicit Bilayer
Abstract
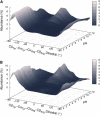
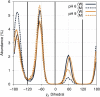
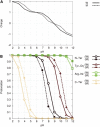
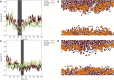
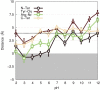
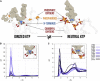
To our knowledge, we present the first constant-pH molecular dynamics study of the neuropeptide kyotorphin in the presence of an explicit lipid bilayer. The overall conformation freedom of the peptide was found to be affected by the interaction with the membrane, in accordance with previous results using different methodologies. Analysis of the interactions between the N-terminus amine group of the peptide and several lipid atoms shows that the membrane is able to stabilize both ionized and neutral forms of kyotorphin, resulting in a pKa value that is similar to the one obtained in water. This illustrates how a detailed molecular model of the membrane leads to rather different results than would be expected from simply regarding it as a low-dielectric slab.
Copyright © 2015 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Berg J.M., Tymoczko J.L., Stryer L. W. H. Freeman; San Francisco, CA: 2002. Biochemistry, Fifth Edition: International Version.
-
- Machuqueiro M., Baptista A.M. Acidic range titration of HEWL using a constant-pH molecular dynamics method. Proteins. 2008;72:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Machuqueiro M., Baptista A.M. Molecular dynamics at constant pH and reduction potential: application to cytochrome c(3) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:12586–12594. - PubMed
-
- Machuqueiro M., Campos S.R.R., Baptista A.M. Membrane-induced conformational changes of kyotorphin revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2010;114:11659–11667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

