Anomalous extracellular diffusion in rat cerebellum
- PMID: 25954895
- PMCID: PMC4423038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.02.034
Anomalous extracellular diffusion in rat cerebellum
Abstract
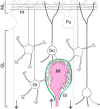
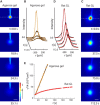
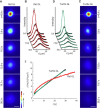
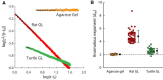
Extracellular space (ECS) is a major channel transporting biologically active molecules and drugs in the brain. Diffusion-mediated transport of these substances is hindered by the ECS structure but the microscopic basis of this hindrance is not fully understood. One hypothesis proposes that the hindrance originates in large part from the presence of dead-space (DS) microdomains that can transiently retain diffusing molecules. Because previous theoretical and modeling work reported an initial period of anomalous diffusion in similar environments, we expected that brain regions densely populated by DS microdomains would exhibit anomalous extracellular diffusion. Specifically, we targeted granular layers (GL) of rat and turtle cerebella that are populated with large and geometrically complex glomeruli. The integrative optical imaging (IOI) method was employed to evaluate diffusion of fluorophore-labeled dextran (MW 3000) in GL, and the IOI data analysis was adapted to quantify the anomalous diffusion exponent dw from the IOI records. Diffusion was significantly anomalous in rat GL, where dw reached 4.8. In the geometrically simpler turtle GL, dw was elevated but not robustly anomalous (dw = 2.6). The experimental work was complemented by numerical Monte Carlo simulations of anomalous ECS diffusion in several three-dimensional tissue models containing glomeruli-like structures. It demonstrated that both the duration of transiently anomalous diffusion and the anomalous exponent depend on the size of model glomeruli and the degree of their wrapping. In conclusion, we have found anomalous extracellular diffusion in the GL of rat cerebellum. This finding lends support to the DS microdomain hypothesis. Transiently anomalous diffusion also has a profound effect on the spatiotemporal distribution of molecules released into the ECS, especially at diffusion distances on the order of a few cell diameters, speeding up short-range diffusion-mediated signals in less permeable structures.
Copyright © 2015 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

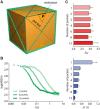
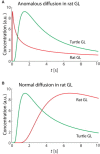
Comment in
-
Anomalous diffusion inspires anatomical insights.Biophys J. 2015 May 5;108(9):2091-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.03.043. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25954865 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Extracellular diffusion is fast and isotropic in the stratum radiatum of hippocampal CA1 region in rat brain slices.Hippocampus. 2005;15(4):441-50. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20068. Hippocampus. 2005. PMID: 15719413
-
Diffusion of epidermal growth factor in rat brain extracellular space measured by integrative optical imaging.J Neurophysiol. 2004 Dec;92(6):3471-81. doi: 10.1152/jn.00352.2004. Epub 2004 Jul 21. J Neurophysiol. 2004. PMID: 15269225
-
Gliotoxin-induced swelling of astrocytes hinders diffusion in brain extracellular space via formation of dead-space microdomains.Glia. 2014 Jul;62(7):1053-65. doi: 10.1002/glia.22661. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24687699 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion of molecules in brain extracellular space: theory and experiment.Prog Brain Res. 2000;125:129-54. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)25007-3. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11098654 Review.
-
Contribution of dead-space microdomains to tortuosity of brain extracellular space.Neurochem Int. 2004 Sep;45(4):467-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2003.11.011. Neurochem Int. 2004. PMID: 15186912 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Extracellular Space of the Brain: From Super-resolved Microstructure to In Vivo Function.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 31;38(44):9355-9363. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1664-18.2018. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30381427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simulation Study on the Mechanism of Intermediate Subdiffusion of Diffusive Particles in Crowded Systems.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 7;8(37):34188-34195. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05945. eCollection 2023 Sep 19. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37744832 Free PMC article.
-
Integrity of White Matter is Compromised in Mice with Hyaluronan Deficiency.Neurochem Res. 2020 Jan;45(1):53-67. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02819-z. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 31175541 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the Prediction of Local Drug Distribution Profiles in the Brain with a New 2D Mathematical Model.Bull Math Biol. 2019 Sep;81(9):3477-3507. doi: 10.1007/s11538-018-0469-4. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Bull Math Biol. 2019. PMID: 30091104 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition with integrated computational and experimental approaches.Phys Biol. 2019 Mar 7;16(3):031001. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/ab0032. Phys Biol. 2019. PMID: 30665206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nicholson C. Diffusion and related transport mechanisms in brain tissue. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2001;64:815–884.
-
- Hrabetova S., Nicholson C. Contribution of dead-space microdomains to tortuosity of brain extracellular space. Neurochem. Int. 2004;45:467–477. - PubMed
-
- Tao L., Nicholson C. Maximum geometrical hindrance to diffusion in brain extracellular space surrounding uniformly spaced convex cells. J. Theor. Biol. 2004;229:59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

