Use of Hybridization Chain Reaction-Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization To Track Gene Expression by Both Partners during Initiation of Symbiosis
- PMID: 25956763
- PMCID: PMC4551195
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00890-15
Use of Hybridization Chain Reaction-Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization To Track Gene Expression by Both Partners during Initiation of Symbiosis
Abstract
The establishment of a productive symbiosis between Euprymna scolopes, the Hawaiian bobtail squid, and its luminous bacterial symbiont, Vibrio fischeri, is mediated by transcriptional changes in both partners. A key challenge to unraveling the steps required to successfully initiate this and many other symbiotic associations is characterization of the timing and location of these changes. We report on the adaptation of hybridization chain reaction-fluorescent in situ hybridization (HCR-FISH) to simultaneously probe the spatiotemporal regulation of targeted genes in both E. scolopes and V. fischeri. This method revealed localized, transcriptionally coregulated epithelial cells within the light organ that responded directly to the presence of bacterial cells while, at the same time, provided a sensitive means to directly show regulated gene expression within the symbiont population. Thus, HCR-FISH provides a new approach for characterizing habitat transition in bacteria and for discovering host tissue responses to colonization.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
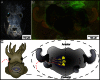
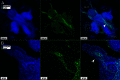

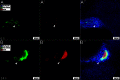


Similar articles
-
Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Regulation Induces Morphological Change in a Key Host Tissue during the Euprymna scolopes-Vibrio fischeri Symbiosis.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0240221. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02402-21. Epub 2021 Sep 28. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34579565 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Histidine Kinase BinK Represses Vibrio fischeri Biofilm Signaling at Multiple Developmental Stages.J Bacteriol. 2021 Jul 8;203(15):e0015521. doi: 10.1128/JB.00155-21. Epub 2021 Jul 8. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34031036 Free PMC article.
-
Using Colonization Assays and Comparative Genomics To Discover Symbiosis Behaviors and Factors in Vibrio fischeri.mBio. 2020 Mar 3;11(2):e03407-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03407-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32127462 Free PMC article.
-
Host/microbe interactions revealed through "omics" in the symbiosis between the Hawaiian bobtail squid Euprymna scolopes and the bioluminescent bacterium Vibrio fischeri.Biol Bull. 2012 Aug;223(1):103-11. doi: 10.1086/BBLv223n1p103. Biol Bull. 2012. PMID: 22983036 Review.
-
Insights into flagellar function and mechanism from the squid-vibrio symbiosis.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019 Oct 25;5(1):32. doi: 10.1038/s41522-019-0106-5. eCollection 2019. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019. PMID: 31666982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Experimentally-validated correlation analysis reveals new anaerobic methane oxidation partnerships with consortium-level heterogeneity in diazotrophy.ISME J. 2021 Feb;15(2):377-396. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00757-1. Epub 2020 Oct 15. ISME J. 2021. PMID: 33060828 Free PMC article.
-
HbtR, a Heterofunctional Homolog of the Virulence Regulator TcpP, Facilitates the Transition between Symbiotic and Planktonic Lifestyles in Vibrio fischeri.mBio. 2020 Sep 1;11(5):e01624-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01624-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32873761 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing the hybridization chain reaction-fluorescence in situ hybridization (HCR-FISH) protocol for detection of microbes in sediments.Mar Life Sci Technol. 2021 Apr 30;3(4):529-541. doi: 10.1007/s42995-021-00098-8. eCollection 2021 Nov. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 37073263 Free PMC article.
-
The Vibrio-Squid Symbiosis as a Model for Studying Interbacterial Competition.mSystems. 2019 Jun 11;4(3):e00108-19. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00108-19. mSystems. 2019. PMID: 31186308 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial symbiont subpopulations have different roles in a deep-sea symbiosis.Elife. 2021 Jan 6;10:e58371. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58371. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33404502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chun CK, Troll JV, Koroleva I, Brown B, Manzella L, Snir E, Almabrazi H, Scheetz TE, de Fatima Bonaldo M, Casavant TL, Soares MB, Ruby EG, McFall-Ngai MJ. 2008. Effects of colonization, luminescence, and autoinducer on host transcription during development of the squid-vibrio association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:11323–11328. doi:10.1073/pnas.0802369105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kremer N, Philipp EE, Carpentier MC, Brennan CA, Kraemer L, Altura MA, Augustin R, Hasler R, Heath-Heckman EA, Peyer SM, Schwartzman J, Rader BA, Ruby EG, Rosenstiel P, McFall-Ngai MJ. 2013. Initial symbiont contact orchestrates host-organ-wide transcriptional changes that prime tissue colonization. Cell Host Microbe 14:183–194. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

