Stoichiometric Assembly of the Cellulosome Generates Maximum Synergy for the Degradation of Crystalline Cellulose, as Revealed by In Vitro Reconstitution of the Clostridium thermocellum Cellulosome
- PMID: 25956772
- PMCID: PMC4551175
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00772-15
Stoichiometric Assembly of the Cellulosome Generates Maximum Synergy for the Degradation of Crystalline Cellulose, as Revealed by In Vitro Reconstitution of the Clostridium thermocellum Cellulosome
Abstract
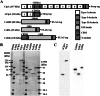
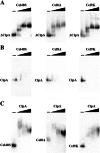
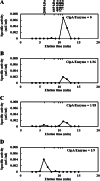
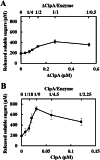
The cellulosome is a supramolecular multienzyme complex formed by species-specific interactions between the cohesin modules of scaffoldin proteins and the dockerin modules of a wide variety of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes. Cellulosomal enzymes bound to the scaffoldin protein act synergistically to degrade crystalline cellulose. However, there have been few attempts to reconstitute intact cellulosomes due to the difficulty of heterologously expressing full-length scaffoldin proteins. We describe the synthesis of a full-length scaffoldin protein containing nine cohesin modules, CipA; its deletion derivative containing two cohesin modules, ΔCipA; and three major cellulosomal cellulases, Cel48S, Cel8A, and Cel9K, of the Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome. The proteins were synthesized using a wheat germ cell-free protein synthesis system, and the purified proteins were used to reconstitute cellulosomes. Analysis of the cellulosome assembly using size exclusion chromatography suggested that the dockerin module of the enzymes stoichiometrically bound to the cohesin modules of the scaffoldin protein. The activity profile of the reconstituted cellulosomes indicated that cellulosomes assembled at a CipA/enzyme molar ratio of 1/9 (cohesin/dockerin = 1/1) and showed maximum synergy (4-fold synergy) for the degradation of crystalline substrate and ∼2.4-fold-higher synergy for its degradation than minicellulosomes assembled at a ΔCipA/enzyme molar ratio of 1/2 (cohesin/dockerin = 1/1). These results suggest that the binding of more enzyme molecules on a single scaffoldin protein results in higher synergy for the degradation of crystalline cellulose and that the stoichiometric assembly of the cellulosome, without excess or insufficient enzyme, is crucial for generating maximum synergy for the degradation of crystalline cellulose.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enzymatic diversity of the Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome is crucial for the degradation of crystalline cellulose and plant biomass.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 19;6:35709. doi: 10.1038/srep35709. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27759119 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Regulation of the Primary Scaffoldin Gene in Clostridium thermocellum.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Mar 31;83(8):e03088-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03088-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28159788 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose hydrolysis ability of a Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome containing small-size scaffolding protein CipA.J Biotechnol. 2015 Oct 20;212:144-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.08.016. Epub 2015 Aug 21. J Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26302838
-
Cellulosomes: bacterial nanomachines for dismantling plant polysaccharides.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017 Feb;15(2):83-95. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.164. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27941816 Review.
-
Cellulosomes-structure and ultrastructure.J Struct Biol. 1998 Dec 15;124(2-3):221-34. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1998.4065. J Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 10049808 Review.
Cited by
-
Determination of the native features of the exoglucanase Cel48S from Clostridium thermocellum.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018 Jan 13;11:6. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-1009-4. eCollection 2018. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018. PMID: 29344087 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic diversity of the Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome is crucial for the degradation of crystalline cellulose and plant biomass.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 19;6:35709. doi: 10.1038/srep35709. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27759119 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of hypothetical scaffolding-like protein S1 in multienzyme complex produced by Paenibacillus curdlanolyticus B-6.AMB Express. 2019 Oct 31;9(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0896-0. AMB Express. 2019. PMID: 31673804 Free PMC article.
-
Inducing effects of cellulosic hydrolysate components of lignocellulose on cellulosome synthesis in Clostridium thermocellum.Microb Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;11(5):905-916. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13293. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Microb Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29943510 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing the composition of a synthetic cellulosome complex for the hydrolysis of softwood pulp: identification of the enzymatic core functions and biochemical complex characterization.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018 Aug 9;11:220. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1220-y. eCollection 2018. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018. PMID: 30116297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raman B, Chongle P, Hurst GB, Rodriguez M, McKeown CM, Lankford PK, Samatova NF, Mielenz JR. 2009. Impact of pretreated switchgrass and biomass carbohydrates on Clostridium thermocellum ATCC 27405 cellulosome composition: a quantitative proteomic analysis. PLoS One 4:e5271. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005271. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

