Protective effect of high concentration of BN52021 on retinal contusion in cat eyes
- PMID: 25956877
- PMCID: PMC4440277
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-015-0030-2
Protective effect of high concentration of BN52021 on retinal contusion in cat eyes
Abstract
Background: Blunt injuries/contusion on eyes might cause retina blunt trauma. This study is to evaluate the protective function of BN52021 against retinal trauma.
Methods: A total of 70 cats, 6 months old, were divided into six groups: Group A to E (n = 12) and normal control (N) group (n = 10). The right eyes in Group A to E were contused. All experiments were performed under general anesthetization. Retrobulbar injections of medication in right eyes were performed. Cats were administrated with 0.5 mL of normal saline (NS), dimethyl sulphoxide, 0.2 g/L BN52021, 1 g/L BN52021 and 5 g/L BN52021, respectively. Cats in Group N were administrated with 0.5 mL of NS. Intraocular pressure (IOP), flash electroretinogram (ERG), and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness were measured. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and transmission electron microscope (TEM) were detected.
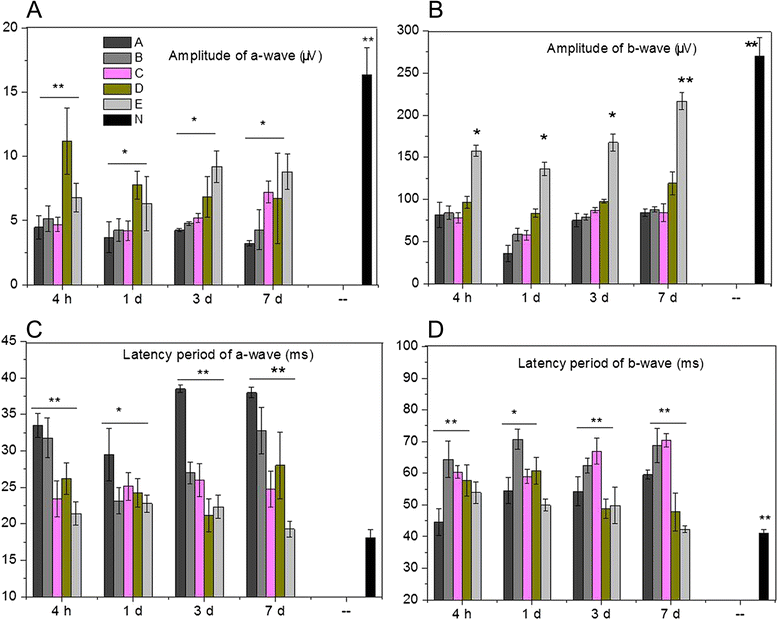
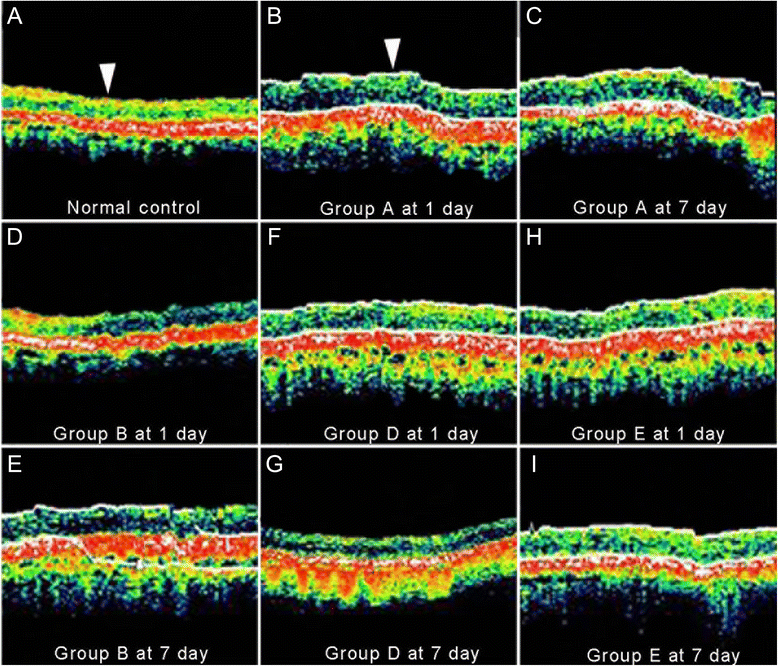
Results: No significant difference was observed in IOP levels among groups. Comparing with cats in Group N, those in Group A to E showed significant lower amplitudes of rod a- and b-waves (P < 0.05). Amplitudes of rod a- and b-waves were increased by administration of high concentration of BN52021 (≥ 1 g/L). Moreover, high concentration of BN52021 decreased the RNFL thickness increased by contusion. Axons in RNFL in Group E arranged neatly at 7 days after modeling.
Conclusions: The degenerated axons caused by contusion were repaired by BN52021. The administration of high concentration of (≥ 1 g/L) BN52021 could partially repair retinal function in contused cat eyes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Relating Retinal Ganglion Cell Function and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer (RNFL) Retardance to Progressive Loss of RNFL Thickness and Optic Nerve Axons in Experimental Glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Jun;56(6):3936-44. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16548. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26087359 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of the retinal nerve fibre layer and reduced retinal function assessed by optical coherence tomography and full-field electroretinography in patients exposed to vigabatrin medication.Acta Ophthalmol. 2014 Mar;92(2):149-57. doi: 10.1111/aos.12030. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 23387307
-
Change of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in various retinal diseases treated with multiple intravitreal antivascular endothelial growth factor.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Apr 15;55(4):2403-11. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13769. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24609624 Clinical Trial.
-
Deformation of the rodent optic nerve head and peripapillary structures during acute intraocular pressure elevation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Aug 22;52(9):6651-61. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7578. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21730343
-
Reproducibility of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using the eye tracker and the retest function of Spectralis SD-OCT in glaucomatous and healthy control eyes.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 May 18;52(6):3338-44. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6611. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21330656
References
-
- Samuel MA, Tawansy KA. Pediatric Retina. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer; 2011. Pediatric Retinal Trauma; pp. 423–31.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

