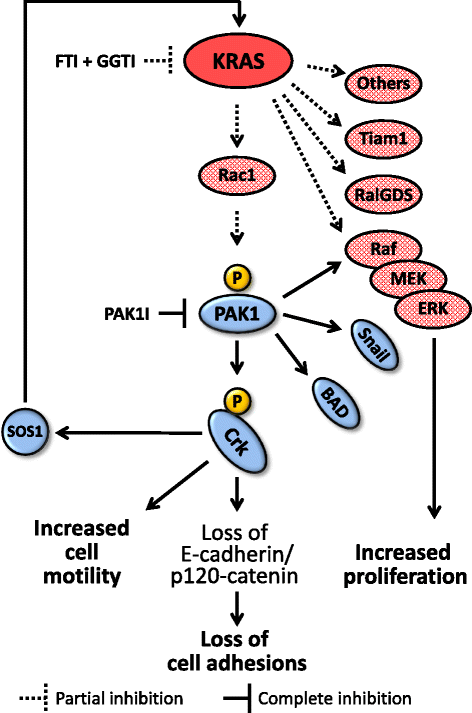
Significance of KRAS/PAK1/Crk pathway in non-small cell lung cancer oncogenesis
- PMID: 25956913
- PMCID: PMC4477307
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1360-4
Significance of KRAS/PAK1/Crk pathway in non-small cell lung cancer oncogenesis
Abstract
Background: Key effector(s) of mutated KRAS in lung cancer progression and metastasis are unknown. Here we investigated the role of PAK1/Crk axis in transduction of the oncogenic KRAS signal in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
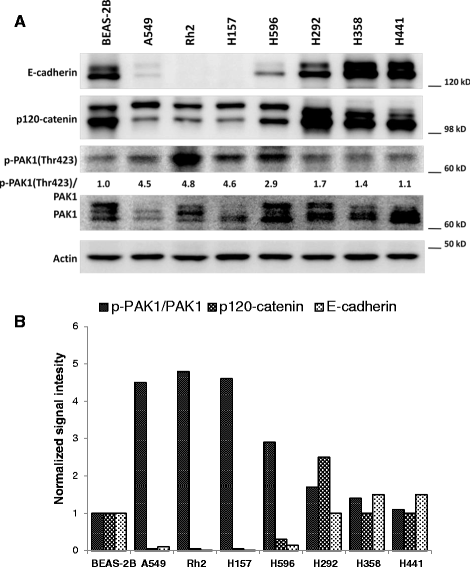
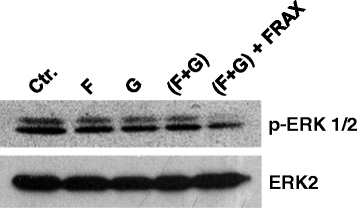
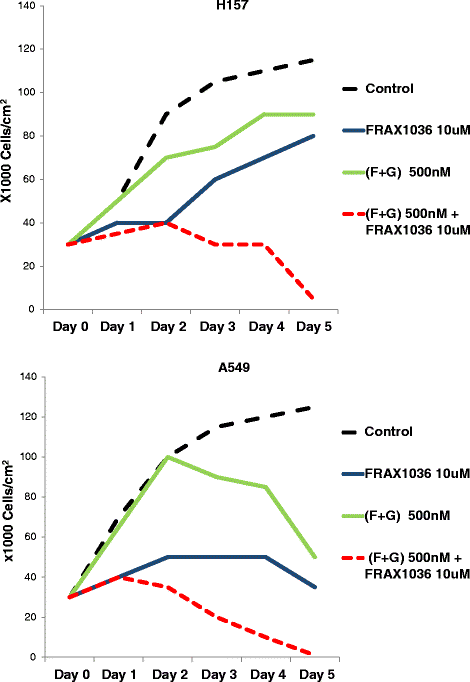
Methods: We used NSCLC clinical specimens to examine the correlation among KRAS mutations (codon 12, 13 and 61); PAK1/Crk axis activation [p-PAK1(Thr423), p-Crk(Ser41)]; and adhesion molecules expression by immunohistochemistry. For assessing the role of proto-oncogene c-Crk as a KRAS effector, we inhibited KRAS in NSCLC cells by a combination of farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) and geranylgeranyltransferase inhibitor (GGTI) and measured p-Crk-II(Ser41) by western blotting. Finally, we disrupted the signaling network downstream of KRAS by blocking KRAS/PAK1/Crk axis with PAK1 inhibitors (i.e., IPA-3, FRAX597 or FRAX1036) along with partial inhibition of all other KRAS effectors by prenylation inhibitors (FTI + GGTI) and examined the motility, morphology and proliferation of the NSCLC cells.
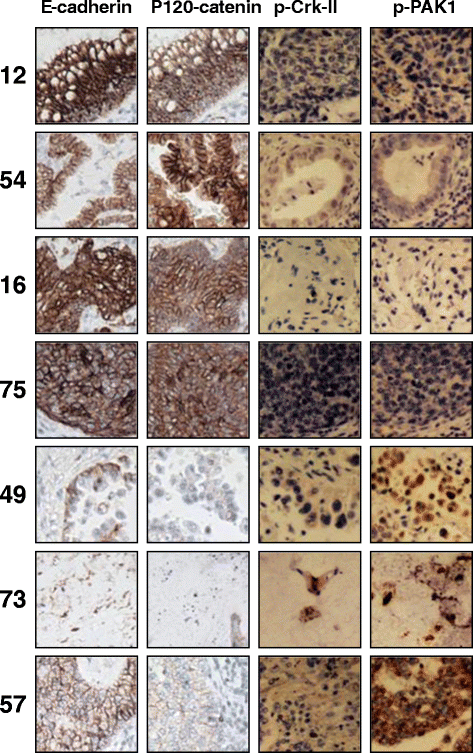
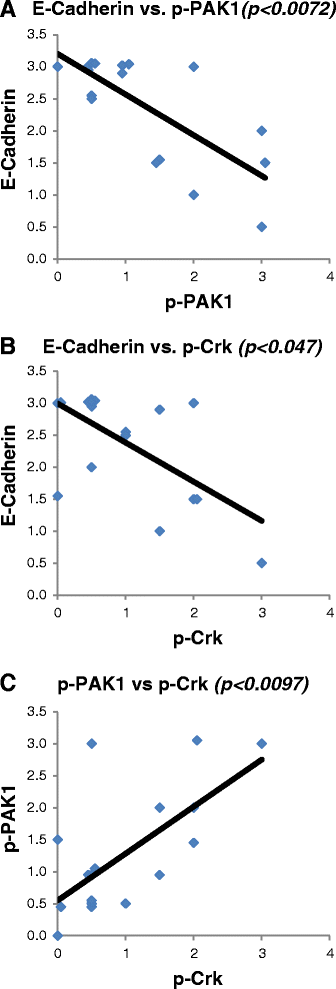
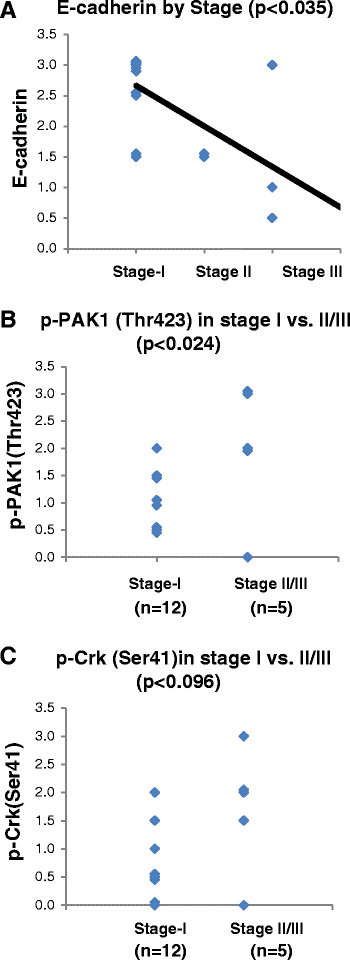
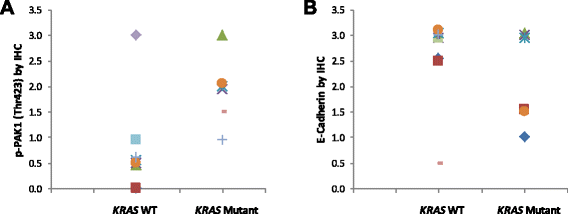
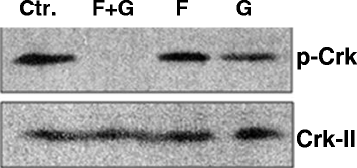
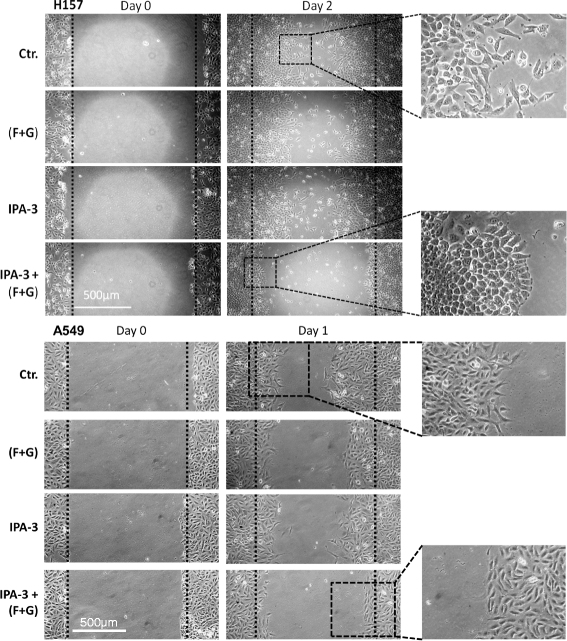
Results: Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated an inverse correlation between PAK1/Crk phosphorylation and E-cadherin/p120-catenin expression. Furthermore, KRAS mutant tumors expressed higher p-PAK1(Thr423) compared to KRAS wild type. KRAS prenylation inhibition by (FTI + GGTI) completely dephosphorylated proto-oncogene c-Crk on Serine 41 while Crk phosphorylation did not change by individual prenylation inhibitors or diluent. Combination of PAK1 inhibition and partial inhibition of all other KRAS effectors by (FTI + GGTI) dramatically altered morphology, motility and proliferation of H157 and A549 cells.
Conclusions: Our data provide evidence that proto-oncogene c-Crk is operative downstream of KRAS in NSCLC. Previously we demonstrated that Crk receives oncogenic signals from PAK1. These data in conjunction with the work of others that have specified the role of PAK1 in transduction of KRAS signal bring forward the importance of KRAS/PAK1/Crk axis as a prominent pathway in the oncogenesis of KRAS mutant lung cancer.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

